As said on the previous page vitiligo can affect everyone, no matter the race, gender, or age – although in most cases the first patches and/or macules are often spotted before the age of 30. There are also a few factors that increase your chances of getting this condition. These risk factors include: having diabetes type 1, anemia, lupus, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and/or thyroid disease. Fortunately, vitiligo isn’t painful, but it can be visible to others which can be stressful for the patient.
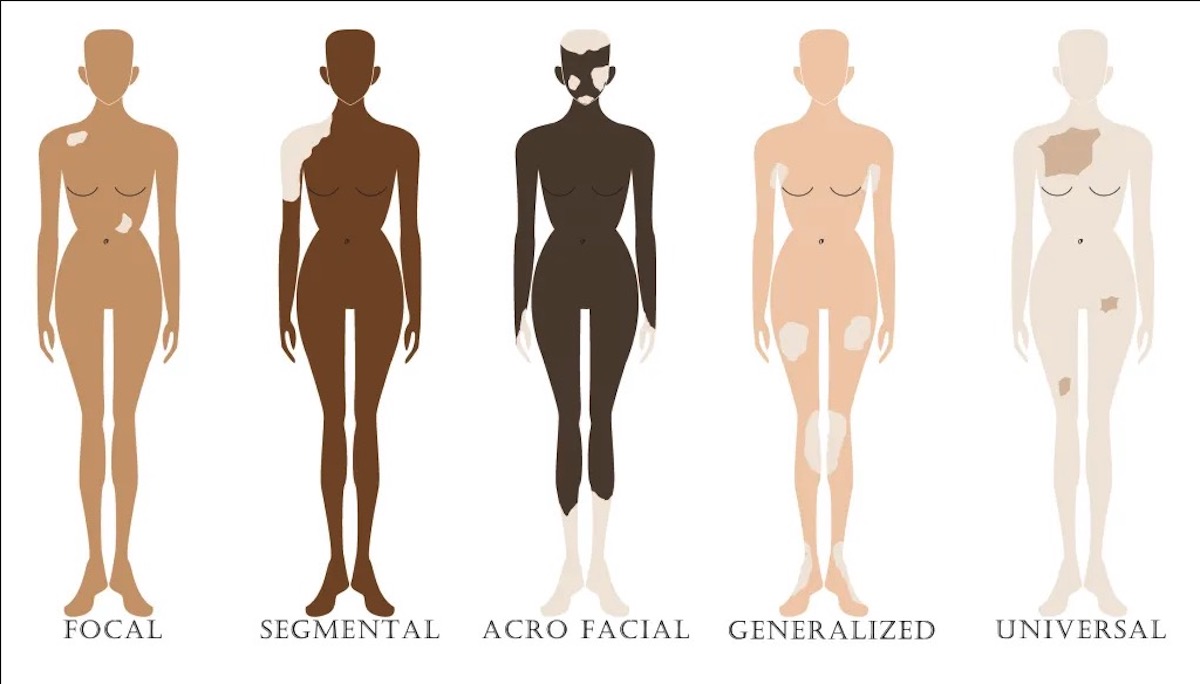
Symptoms of Vitiligo
As this is a skin condition, the symptoms are visible on the skin. The most obvious symptom is the loss of skin or hair color or pigmentation. Places you can check yourself are:
- Body folds, like the knees & armpits
- Skin areas that have been injured before
- Skin areas exposed to UV/ sunlight, like the face, hands, and fingers
- Around moles
- Around body openings, like the belly button
- Skin areas around your nose and mouth also called mucous membranes
Treatment options
There isn’t a cure (yet) for vitiligo. Once the lighter or white macules or patches start to form it’s very rare for the pigment to return to the affected area. Treatment is focused on making the skin look better. Possible treatment options include:
- Medication
- Light therapy
- Depigmentation therapy
- Surgery
- Counseling for a healthy and confident mind
It’s important to always seek medical treatment when you suffer – or think you suffer – from a skin disorder. Your healthcare provider will take a good look at you, exam your symptoms, set the right diagnosis, and start an effective treatment plan. There are so many types of skin disorders, vitiligo is just the tip of the iceberg. This is why it’s important to do your own online research first. We are here to help you, so start your search here

