Poison ivy rash is a skin condition that affects many people in the United States. It’s caused by an allergic reaction to the sap of the poison ivy plant. Which is found in most regions of the country. Let’s take a closer look at what this condition is, its causes and types, and how it can be treated.
What is Poison Ivy Rash?
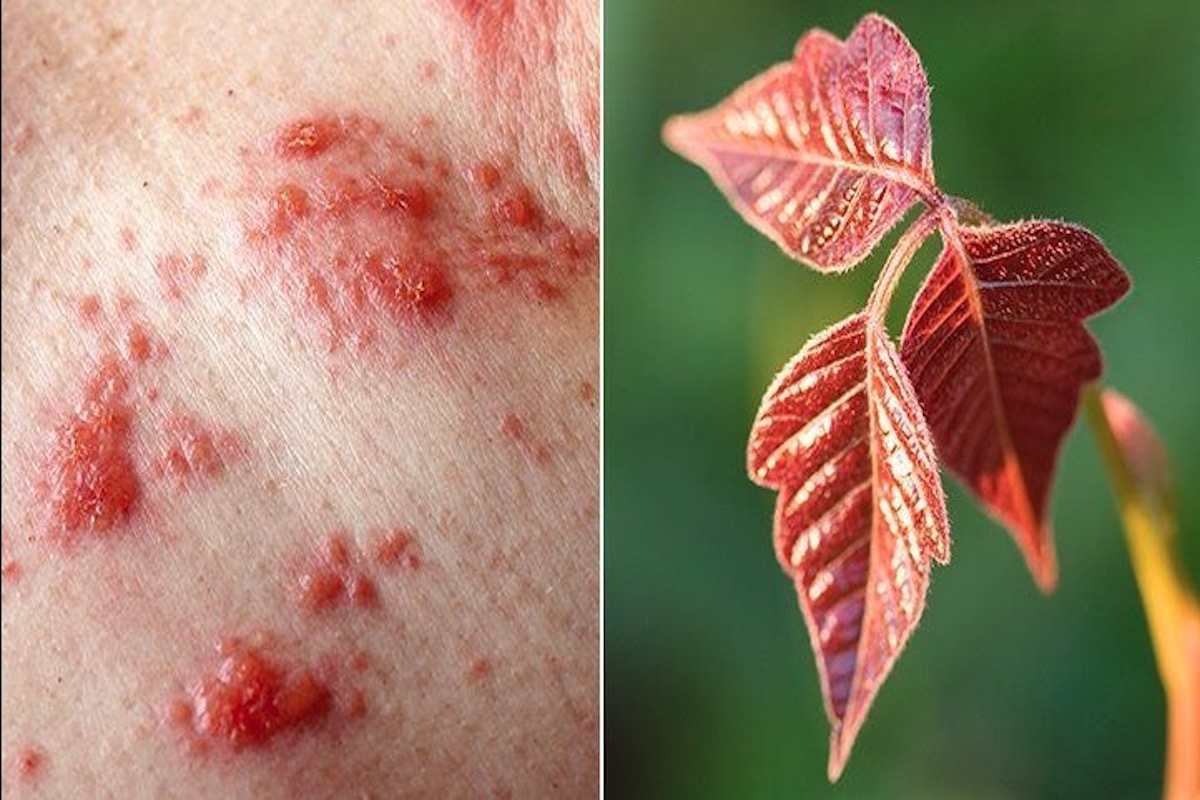
Poison ivy rash is a skin condition that occurs when a person comes into contact with the sap of the poison ivy plant. The sap contains a toxic substance called urushiol, which can cause an allergic reaction when it comes into contact with the skin.
Causes & Types of Poison Ivy Rash
Poison ivy rash is caused by an allergic reaction to urushiol, which is found in all parts of the poison ivy plant, including the leaves, stems, and roots. There are several types, including mild, moderate, and severe reactions. Mild reactions typically involve redness and itching of the skin, while severe reactions can cause swelling, blistering, and difficulty breathing.
Who Is At Risk?
Anyone can develop this kind of rash, but some people are more at risk than others. People who spend time outdoors, such as hikers and gardeners, are more likely to come into contact with the poison ivy plant. Additionally, people who are allergic to other plants may also be more susceptible to developing this.
Symptoms of Poison Ivy Rash
Symptoms of this kind of rash include redness, itching, and blistering of the skin. The rash usually appears in a straight line or streak, corresponding to the area where the skin came into contact with the urushiol. In some cases, the rash may spread to other areas of the body if the person touches the affected area and then touches other parts of the skin.
Overview of Different Types of Poison Ivy Rash
This table provides an easy-to-read summary of the various types of poison ivy rash, including their appearance, causes, and treatment options. Whether you experience a mild, moderate, or severe reaction to the plant’s urushiol, this table can help you understand what to expect and how to best treat the rash.
| Types | Appearance | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Mild reaction | Redness, itching, and minor bumps on the skin | Topical creams and lotions, such as calamine or hydrocortisone, cool compresses, and oral antihistamines |
| Moderate reaction | More extensive rash with increased swelling, redness, and blisters | Prescription-strength topical or oral medications, such as corticosteroids or antihistamines |
| Severe reaction | Widespread rash with severe blistering and swelling, sometimes accompanied by fever or difficulty breathing | Immediate medical attention, including prescription-strength medications, such as corticosteroids or antihistamines, and in rare cases, hospitalization |
How Is It Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider can usually diagnose poison ivy rash by examining the affected area and asking about the person’s exposure to the poison ivy plant. In some cases, a sample of the rash may be taken for testing to rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Poison Ivy Rash
Most cases can be treated with home remedies and over-the-counter medications. These include:
- Washing the affected area with soap and water as soon as possible after exposure
- Applying calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream to reduce itching and inflammation
- Taking an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine to relieve itching and promote sleep
- Avoiding scratching or rubbing the affected area, which can worsen the rash
Sometimes, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications such as corticosteroids or oral antihistamines to treat severe symptoms. In rare cases, hospitalization may be necessary if the person experiences a severe reaction or difficulty breathing.
In conclusion, poison ivy rash can be uncomfortable and unsightly, but can be treated with home remedies and over-the-counter medications. With proper prevention measures, you can reduce your risk of developing it in the future. Still need information about this skin condition, or do your symptoms not match those listed above? Then search further here quickly:

