Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious viral infection that affects the respiratory system. It is one of the leading causes of death among young children worldwide, particularly in developing countries. We will discuss what measles is, its causes and types, who is at risk, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What Is Measles?
Measles is a viral infection caused by a virus that spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and other people breathe in the contaminated droplets. Moreover, the virus can survive on surfaces for up to two hours, making it highly contagious. However, rubeola is preventable through vaccination, and the World Health Organization recommends two doses of the vaccine for all children.
Despite being preventable, an outbreak can be dangerous because it’s a very contagious disease that can easily spread from one person to another. It can make people very sick and cause complications like pneumonia, brain swelling, and even death. Outbreaks can occur when many people in an area are not vaccinated, allowing the disease to spread quickly. This is especially dangerous for young children, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems who are more vulnerable to getting sick.
Causes & Types of Measles
Measles is caused by the rubeola virus, which belongs to the family of paramyxoviruses. There are two types: the wild-type measles virus and the attenuated measles virus used in the vaccine. The wild-type virus is responsible for outbreaks, while the attenuated virus in the vaccine helps protect against the disease.
Who Is At Risk?
Measles can affect anyone, but children under the age of five and adults over the age of 20 are at higher risk. People who have not received the vaccine are also more likely to get infected. This highly contagious disease is more common in areas with poor sanitation and low vaccination rates.
Symptoms of Measles
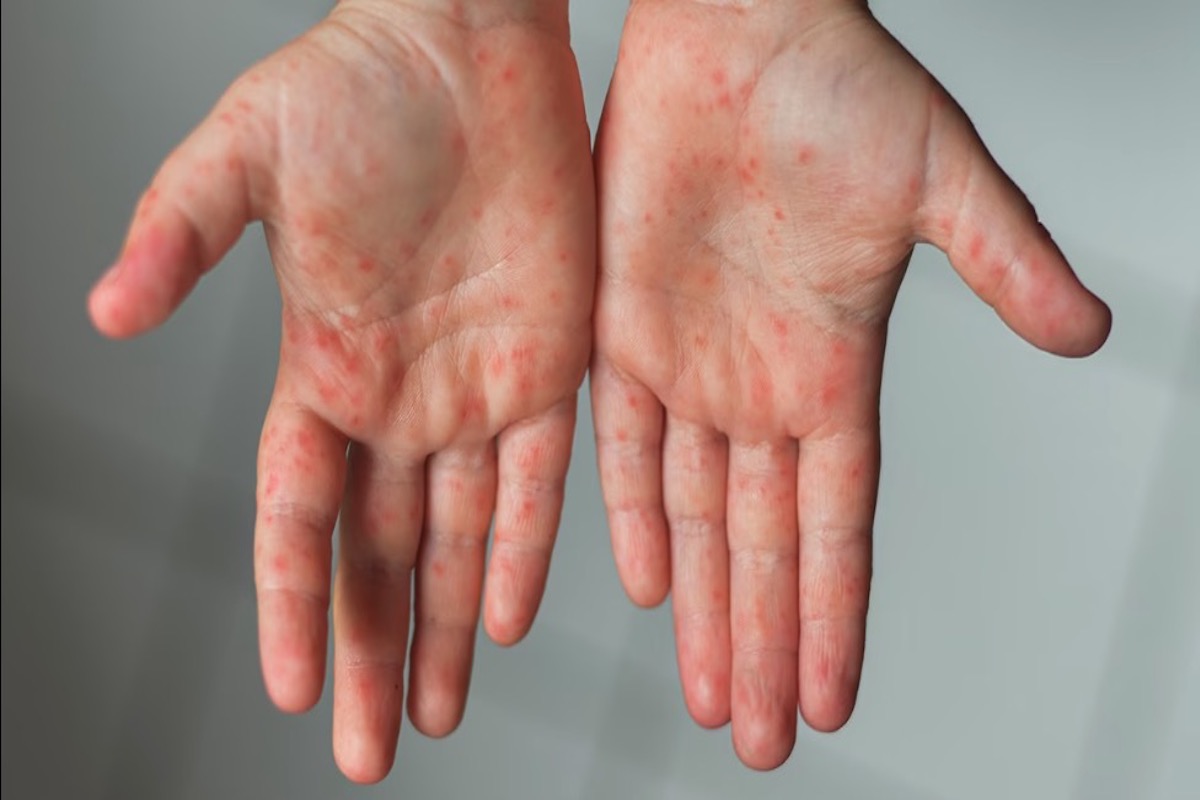
Measles has several symptoms, and they usually start about 10–14 days after a person is exposed to the virus. The first symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose, and red, watery eyes. After a few days, a rash appears on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is made up of flat, red spots that can join together and become raised. Other symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and ear infections. It can be dangerous, and if you or someone you know has symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention right away.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Measles can be diagnosed through a physical exam and a blood test. The doctor will look for the characteristic rash and ask about symptoms and recent travel history. A blood test can confirm the presence of the virus antibodies.
Treatment Options for Measles
There is no specific treatment. The virus usually clears up on its own within two to three weeks. However, treatment is focused on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This may include bed rest, fluids, and fever-reducing medication. Antibiotics may be prescribed for secondary bacterial infections such as ear infections or pneumonia. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
The Importance of Vaccinating Your Children Against Measles
Vaccinating your children against measles is very important to keep them safe and healthy. As mentioned earlier, it is very contagious and can make children very sick. These vaccines protect against measles and help to stop it from spreading. When more people get vaccinated, it helps to prevent outbreaks and protects those who can’t get vaccinated. Vaccines are safe and work well to keep your child healthy. It is recommended that all children get vaccinated to protect themselves and others.
Measles Outbreak in the United States in the Last 10 Years
This table shows the number of confirmed cases in the United States over the past 10 years, including the states that were affected. It can spread quickly, and outbreaks can occur when many people in an area are not vaccinated. The table helps us to understand the frequency and severity of the disease outbreaks in recent years and highlights the importance of vaccination to prevent the spread of the disease.
| Year | Number of Confirmed Cases in the U.S. | States Affected |
|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 55 | 17 |
| 2013 | 187 | 11 |
| 2014 | 667 | 27 |
| 2015 | 188 | 24 |
| 2016 | 86 | 19 |
| 2017 | 120 | 15 |
| 2018 | 372 | 26 |
| 2019 | 1,282 | 31 |
| 2020 | 1,282* | 50** |
| 2021 | 15 | 8 |
*Note: This number represents the total number of cases reported in the U.S. up until October 2020, when reporting of measles cases was disrupted due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
**Note: All 50 states reported cases in 2020 due to outbreaks in multiple communities.
Measles can cause severe complications, particularly in young children and adults. In case, you suspect you or your child has rubeola, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and spread of the virus. Still need information about this condition, or do your symptoms not match those listed above? Then search further here quickly:

