Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It is one of the most common cancers in the United States, with approximately 61,000 new cases diagnosed each year. This disease can affect both adults and children, making it a significant concern for many. Understanding and know how to recognize this type of cancer is crucial. Diagnosing it sooner improves the chances of getting better.
Causes of Leukemia
Leukemia affects the blood and bone marrow, where blood cells are made. In this case, the body produces abnormal blood cells that grow and divide uncontrollably. These abnormal cells crowd out healthy blood cells, making it hard for the body to work properly. The two most common causes are genetic factors and exposure to high levels of radiation. Genetic factors mean that some people inherit changes in their DNA that increase their risk of getting leukemia. Exposure to high levels of radiation, such as from nuclear accidents or radiation therapy for other cancers, can damage the DNA in blood cells, leading to this type of cancer. Other causes include:
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with certain chemicals like benzene can increase the risk.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can cause mutations in blood cells.
- Previous Cancer Treatments: Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can sometimes lead to leukemia later in life.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Some genetic disorders, like Down syndrome, are linked to a higher risk of leukemia.
- Family History: Having a close relative with leukemia can increase the risk, though this is less common.
Are There Different Types?
There are different types of leukemia. This table gives an easy-to-read overview about the different types. It shows how quickly each type progresses, which blood cells are affected, the age group most commonly affected, and how many new cases are diagnosed each year in the United States. Note: These estimates provide a general idea of how common each type of leukemia is in the United States.
| Type of Leukemia | Progression | Affected Cells | Most Common Age Group | Chance of Getting This Type in America |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) | Rapid | Lymphoid cells | Children | About 6,000 new cases per year |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | Rapid | Myeloid cells | Adults and children | About 20,000 new cases per year |
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Slow | Lymphoid cells | Older adults | About 21,000 new cases per year |
| Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) | Slow | Myeloid cells | Adults | About 8,500 new cases per year |
Certain people are more at risk of getting this type of cancer. Older adults have a higher risk, especially for chronic types like CLL and CML, while children are most commonly affected by Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL). A family history of leukemia can increase risk, as can exposure to high levels of radiation from nuclear accidents or radiation therapy. People exposed to chemicals like benzene, found in gasoline and some industries, and smokers are also at higher risk. Additionally, individuals with certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, or those who have undergone chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other cancers, are more susceptible to developing it.
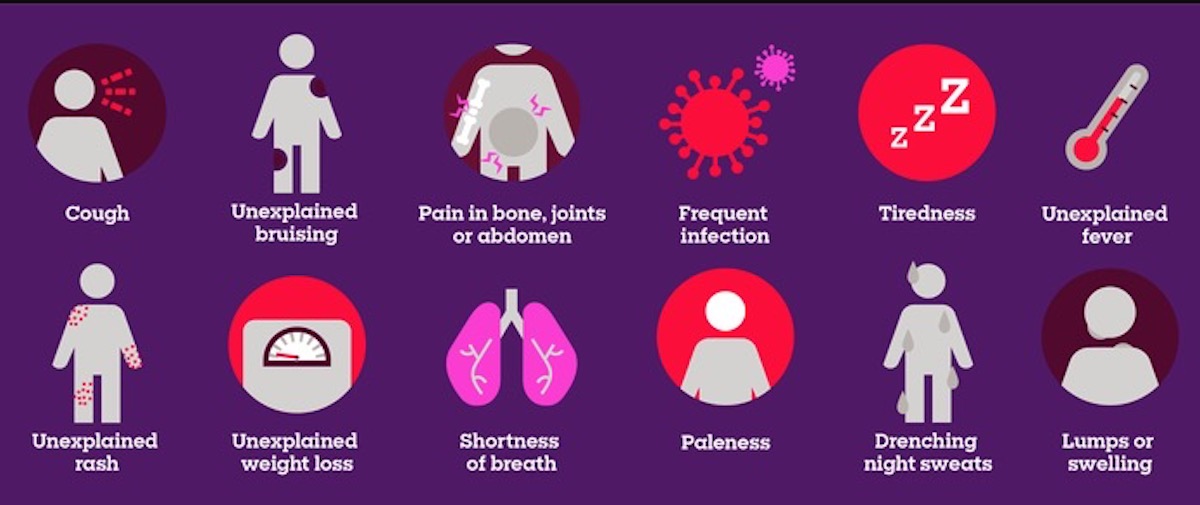
Symptoms to Recognize
How Is It Diagnosed?
Stages & Survival Rates of Leukemia
If doctors diagnose you with this type of cancer, they will tell you how far your cancer has progressed and, if applicable, what stage it is in. This table shows the different types of leukemia, how they are staged, and their 5-year survival rates in the United States. The stages indicate the progression of the disease, while the survival rate shows the percentage of people who live at least five years after diagnosis.
| Type of Leukemia | Stages | 5-Year Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) | Not typically staged | About 69% overall (children: 90%) |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | Not typically staged | About 29% |
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Stages 0 to IV | About 87% |
| Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) | Chronic, Accelerated, Blast Phase | About 70% |
CCL: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Stages: CLL is staged using the Rai or Binet system, ranging from stages 0 to IV.
- Stage 0: High white blood cell count
- Stages I-II: Enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, or liver
- Stage III-IV: Anemia or low platelet count
CML: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Stages: CML is staged based on the phase of the disease:
- Chronic Phase: Few symptoms, responds well to treatment
- Accelerated Phase: More symptoms, disease progresses faster
- Blast Phase: Severe symptoms, high number of immature white blood cells
Read more about CML here: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Treatment Options for Leukemia
This cancer type is treated in several ways, depending on the type and how advanced it is. The two most common treatment options are chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells, while radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. Other treatment options include:
- Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs to target specific parts of cancer cells.
- Biological Therapy: Helps the immune system fight cancer.
- Stem Cell Transplant: Replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy bone marrow from a donor.
- Surgery: Rarely used but can remove a large mass of affected cells.
In children, the treatment plan is often more intensive, especially for Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL). Children may receive higher doses of chemotherapy and may require longer treatment periods. They also usually need more supportive care to manage side effects and ensure healthy development during treatment. If you or a loved one are diagnosed with cancer and are unsatisfied with the treatment plan, it’s wise to seek a second opinion from another hospital or oncology center. Keep exploring to learn more about cancer, the stages of leukemia, and its treatment options. Continue your search here:

