Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States – that’s 1 in 3 deaths. Every 34 seconds, someone dies of heart disease, and every 40 seconds someone is getting a heart attack. This means, therefore, that about 1.5 million heart attacks occur in our country every year. 20% of heart attacks are called ‘silent heart attacks,’ as people are not aware they happened. That’s why it’s important to know what can cause a heart attack and how you can recognize one in yourself and your loved ones. The better informed we are, the sooner we can intervene and prevent serious damage or death.
Causes of a Heart Attack
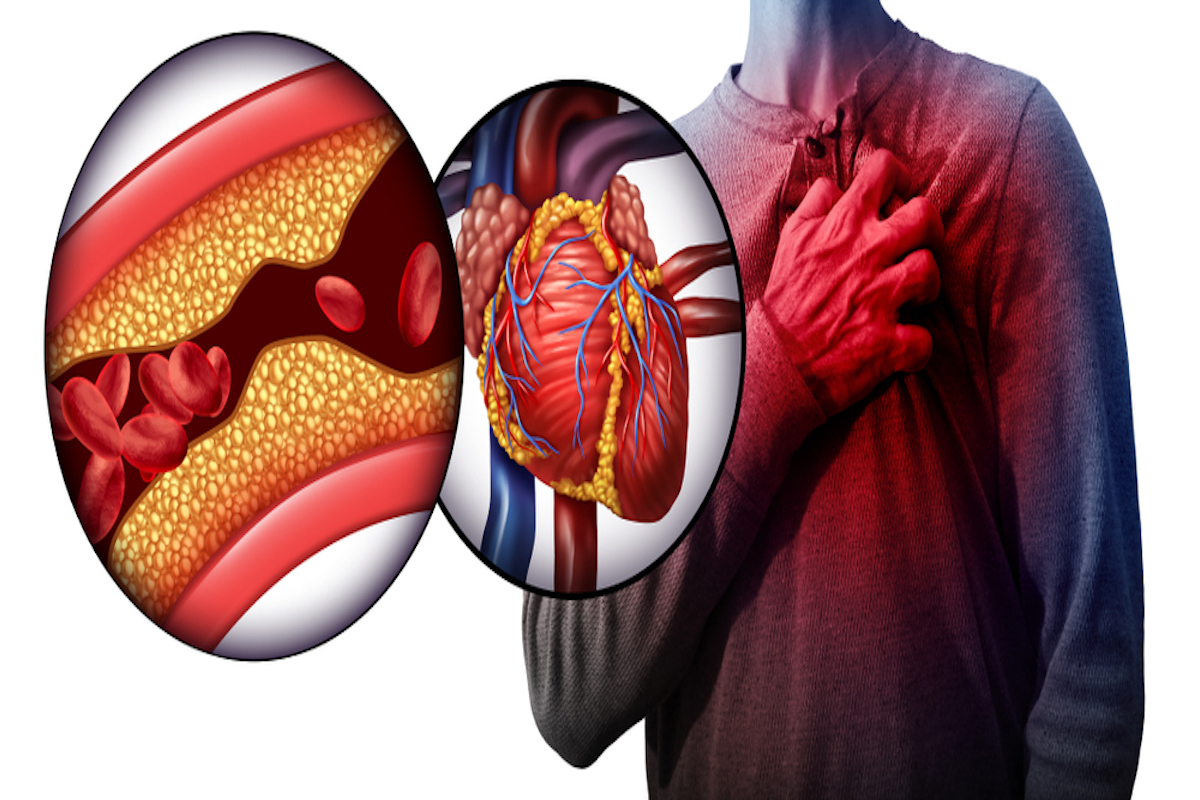
Before we explain what the most common reasons for heart attacks are, it’s good to know what it entails. When the blood flow – with fresh oxygen – via the arteries to the heart is blocked or extremely reduces, part of the heart receives not enough blood, and if this is not dealt with, the heart muscle can suffer severe damage or even stop beating, which can eventually lead to death. The medical term for heart attack is myocardial infarction. In most cases the reason is a CAD – coronary artery disease -, other common causes are severe spasms or sudden contractions of an artery that can stop the blood flow to the heart muscle. But how is this possible?
Risk Factors
CAD is a disease in which the major blood vessels – coronary arteries – that provide blood to the heart become clogged. The thing that clogs the coronary arteries is called deposits of cholesterol or plaque. Moments before you have a heart attack, the following happens: one – or more – of these plaques in the coronary arteries burst, creating a blood clot, which blocks the blood from flowing to the heart, eventually causing you to have a heart attack. You have an increased risk of CAD if you:
- Smoke
- Eat a lot of fat
- Suffer from diabetes
- Have high cholesterol
- Have high blood pressure
- Are overweight or obese
- (Mis)use drugs
- Have lack of oxygen in your blood
Continue reading on the next page and find out how you can recognize a heart attack in women, and what you should do next.

