Gastroparesis – sometimes referred to as delayed gastric emptying – is a medical condition where the stomach muscles don’t work properly, causing delayed emptying of the stomach. This means that food stays in the stomach longer than it should. In the United States, it’s estimated that around 5 million people suffer from Gastroparesis. While it can affect anyone, there are certain risk groups, including individuals with diabetes, those who have undergone certain surgeries, and people with autoimmune disorders or connective tissue disorders. Understanding this condition is crucial to recognize the symptoms and get the right diagnosis and treatment.
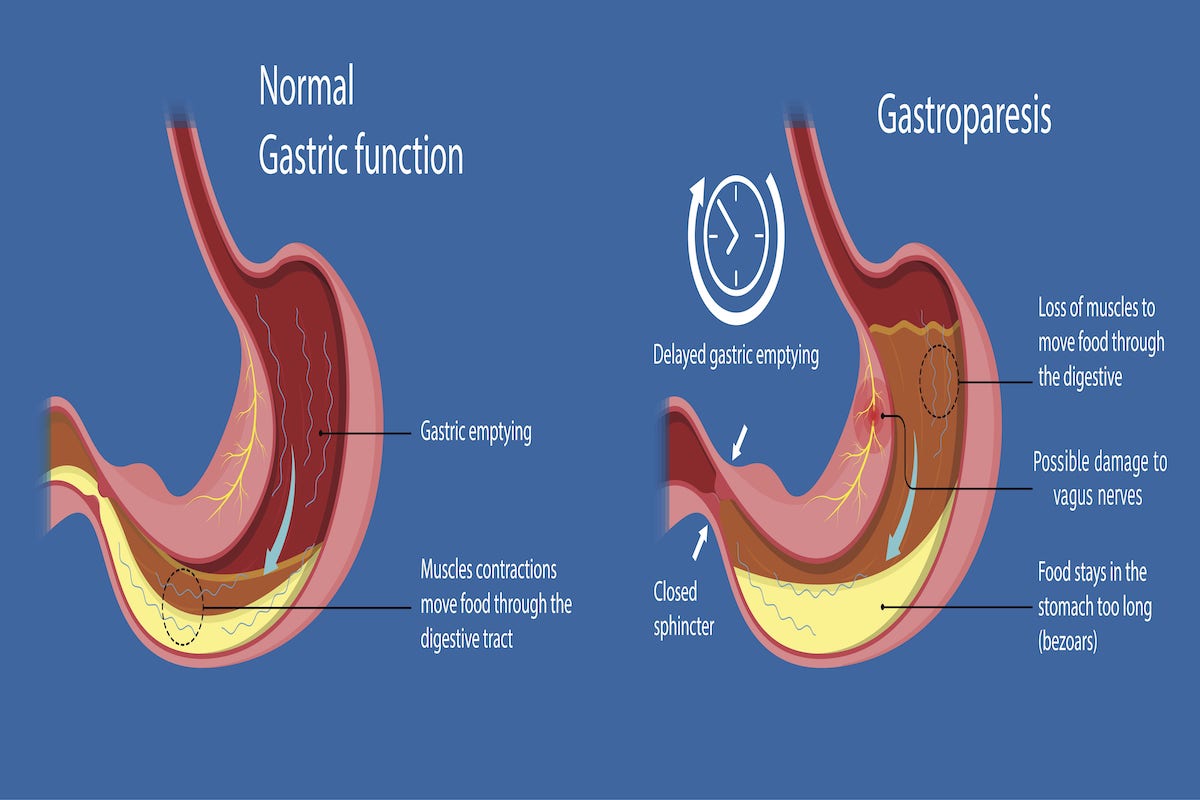
Are There Different Types of Gastroparesis?
Information about the different types of Gastroparesis can be overwhelming. To make it easier to understand, we’ve created this table which explains which types there are, what they entail, and what their prevalence is. Keep in mind that the mentioned prevalence numbers are approximate estimates and can vary.
| Type of Gastroparesis | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Gastroparesis | Associated with diabetes, affects stomach motility. | Prevalence: About 30-50% of people with diabetes. |
| Idiopathic Gastroparesis | Cause is unknown, delayed stomach emptying occurs. | Prevalence: Accounts for around 40-50% of cases. |
| Postsurgical Gastroparesis | Can develop after certain surgical procedures. | Prevalence: Varies based on the type of surgery. |
| Autoimmune Gastroparesis | Immune system mistakenly attacks stomach nerves. | Prevalence: Less common, exact prevalence is unclear. |
| Drug-induced Gastroparesis | Certain medications can slow stomach motility. | Prevalence: Varies based on medication usage. |
| Connective Tissue Disorder-related Gastroparesis | Associated with certain connective tissue disorders. | Prevalence: Less common, prevalence varies by disorder. |
What Causes Gastroparesis?
Gastroparesis can occur due to various factors. One of the primary causes is diabetes, where high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves responsible for controlling the stomach muscles. Additionally, certain medications, such as opioids and antidepressants, can contribute to the development of Gastroparesis. Surgeries involving the stomach or esophagus, such as gastric bypass surgery, can also lead to this condition.
Infections, particularly viral infections, can affect the stomach’s ability to function properly. Hormonal disorders like hypothyroidism and disorders affecting the nervous system, such as Parkinson’s disease, can be associated with Gastroparesis as well. In some cases, the exact cause remains unknown. By understanding the potential causes, healthcare providers can identify the underlying factors contributing to Gastroparesis and tailor treatment approaches accordingly.
It is indeed possible to be misdiagnosed with another gastrointestinal disorder when you actually have Gastroparesis. For instance, the symptoms of Gastroparesis can be mistaken for conditions like GERD or peptic ulcers. These conditions also present with similar symptoms, making it challenging to differentiate them without proper diagnostic tests. In some cases, individuals may receive treatment for these alternative conditions without addressing the underlying delayed gastric emptying, leading to ongoing symptoms and unresolved issues. This is why it’s important to recognize symptoms and explain your suspicions to your professional healthcare provider.
What Are Symptoms of Gastroparesis?
The two most common symptoms are nausea and vomiting. Nausea is a feeling of sickness in the stomach, making you feel like you might throw up. It can be accompanied by an unsettled sensation in the belly. Vomiting, on the other hand, is when you forcefully empty the contents of your stomach through your mouth. It can happen after meals or when you try to eat something. In addition to these, other symptoms include:
- Feeling full quickly
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Poor appetite
- Erratic blood sugar levels
Complication of Undiagnosed Gastroparesis
Unfortunately, if Gastroparesis goes undiagnosed or untreated there are several (serious) complications:
- Malnutrition: Gastroparesis can hinder the proper absorption of nutrients from food, leading to malnutrition and deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Dehydration: In severe cases, frequent vomiting and inadequate fluid intake due to Gastroparesis can result in dehydration, which can further worsen overall health.
- Fluctuations in blood sugar levels: Gastroparesis can interfere with the normal digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, making it challenging to regulate blood sugar levels, especially in individuals with diabetes.
- Bacterial overgrowth: When food remains in the stomach for an extended period, it can promote the growth of bacteria, potentially leading to bacterial overgrowth in the digestive system.
- Gastroesophageal reflux: Delayed emptying of the stomach can contribute to the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Are There Any Treatment Options Available?
Once diagnosed with Gastroparesis, there are several possible treatment options to manage the condition and alleviate symptoms. These options may include:
-
- Dietary modifications: Adjusting the diet by consuming smaller, more frequent meals that are easier to digest. This may involve avoiding high-fat and high-fiber foods that can delay stomach emptying.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to help improve stomach motility, such as prokinetic drugs, which can help stimulate the muscles and enhance stomach emptying.
- Feeding tube: In severe cases where oral intake is insufficient, a feeding tube may be necessary to deliver liquid nutrition directly into the small intestine.
- Managing underlying conditions: If it’s caused by an underlying condition like diabetes, treating and controlling that condition effectively may help manage Gastroparesis symptoms.
- Electrical stimulation: In certain cases, a gastric electrical stimulation device can be implanted to help regulate stomach contractions and improve motility.
By following these tips, you may be able to recognize, prevent or manage the condition. It can be a challenging problem to deal with, but there are solutions available. Identifying the cause and seeking the right treatment for your situation is important. We hope this article has provided helpful information on how to deal with Gastroparesis. For more info on this topic or other tips about gas & bloating start your search here:

