Last year more than 3.5 million children were born in the United States. All these pregnancies have come to an end and are completed successfully. Unfortunately, this isn’t always the matter. Sometimes women get miscarriages or the baby dies in the belly, and the pregnancy is terminated early. These are just some of the outcomes of pregnancy. Another severe but slightly less common outcome is an ectopic pregnancy. Approximately, 1 in 50 pregnancies are ectopic. It’s good for everyone to know exactly what an ectopic pregnancy is when you have an increased risk of this type of pregnancy, whether you can recognize it, and what to do next. Yes even if you are male!
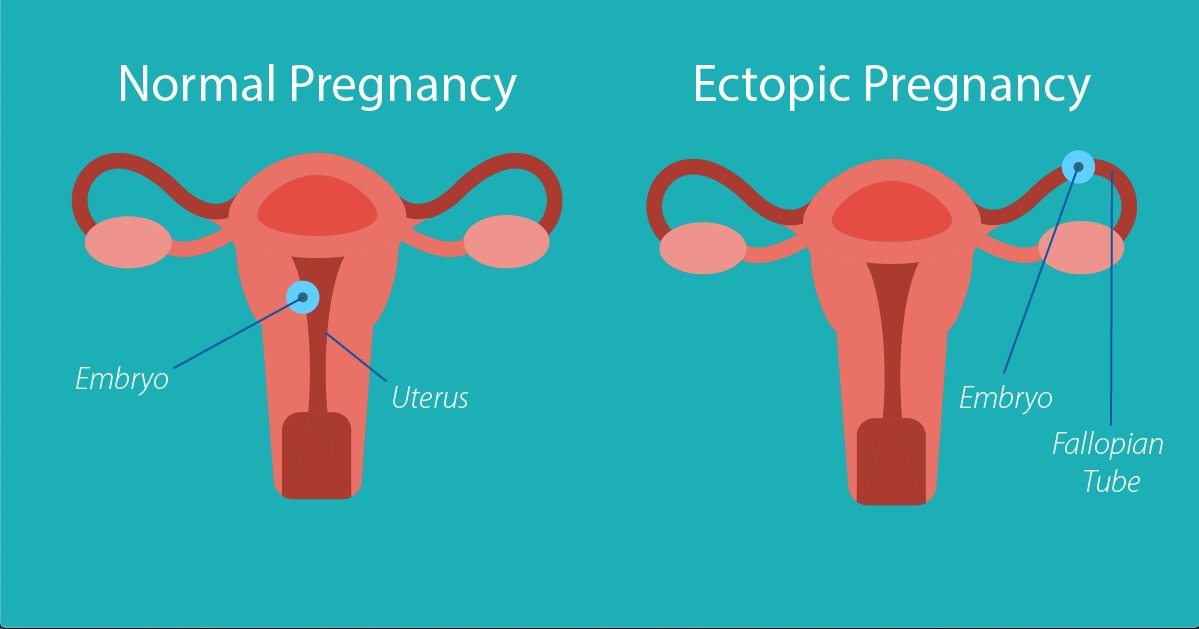
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. The fallopian tube is the most common location, accounting for 90% of cases. Unlike a successful pregnancy, the egg implants in body tissue not designed for fetal growth, which can lead to tissue rupture and threaten the mother’s life. Ectopic pregnancies are not viable and always result in pregnancy loss
Causes & Risk Factors for an Ectopic Pregnancy
There isn’t a specific cause why one pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy and the other one is a normal pregnancy. Often this happens because of conditions that slow down or block the movement of the fertilized egg down from the oviduct through the fallopian tube to the uterus. This can be caused by damaged or misshapen fallopian tube(s), hormonal imbalances, or abnormal growth of the egg. There are a few factors that can increase the risk of getting an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors include:
- Prior ectopic pregnancy
- Inflammation or infections – caused by STDs or pelvic inflammation disease
- Fertility treatments
- Reproductive system surgery – like tubal or ovary surgery
- Pregnancy while using an IUD as birth control
- Smoking
- Endometriosis
- Infertility
We already mentioned how dangerous this kind of pregnancy is. In fact, it is life-threatening for the mother. The fetus will continue to grow, but the tissue in which it is nested is not made for this, so at some point, it will no longer be able to grow with it and rupture. This is the part where it becomes life-threatening because the rupture of, say, the fallopian tube can cause internal bleeding that the mother can die from if it is not detected.
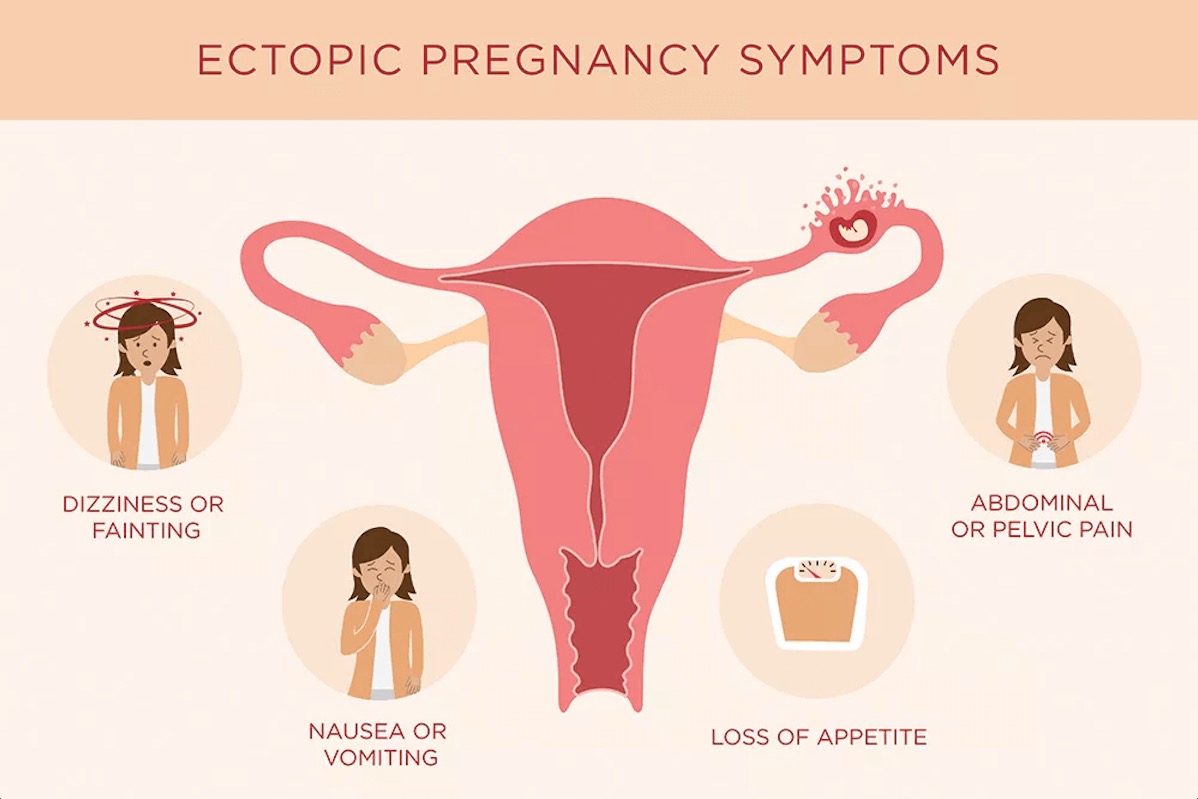
Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy
At first, most women won’t notice any specific symptoms and experience normal pregnancy symptoms like a missed period, nausea, fatigue, and tender breast. Warning signs include:
- Light vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Upset stomach & vomiting
- Sharp abdominal cramps
- Pain on one side of the body
- Dizziness/weakness
- Pain in the shoulder, neck, and/or rectum
In case the ectopic pregnancy is ruptured, symptoms like fainting, (severe) low blood pressure, rectal pressure, shoulder pain, severe (one-sided) abdominal pain, and heavy vaginal bleeding may be experienced. Call your healthcare provider immediately if you experience these symptoms!
Treatment Options
Pregnancies that nest outside the uterus are not viable because it does not get enough space, blood supply, and necessary nutrients. Unfortunately, this kind of pregnancy always ends up in pregnancy loss. If you experience the above-mentioned symptoms, it’s wise to contact your professional healthcare provider and get yourself and your pregnancy checked out. The provider will do some tests, like a pregnancy test, a pelvic exam, and an ultrasound to examine the uterus and the fallopian tubes. In case the pregnancy is an ectopic one, the pregnancy should be terminated. There are 2 treatment options:
- Medication
- Surgery
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot be prevented, but you can try to take into account the risk factors as much as possible, which reduces the chances of this type of pregnancy. Women who had this kind of pregnancy can have a successful pregnancy in the future. For more information about (ectopic) pregnancies, continue your online search here:

