Esophageal cancer may not be as widely discussed as some other types, but it’s an important health topic that deserves our attention. In the United States alone, it affects a significant number of individuals each year, making it a concern for many families and communities. While not considered one of the most common cancers, esophageal cancer still touches the lives of many. Each year, about 20,640 people in the United States are diagnosed with this disease. This makes it important for people to know about it, how to recognize it, and what you should do if you suspect you’re – or someone else – is suffering from it.
What Is Esophageal Cancer?
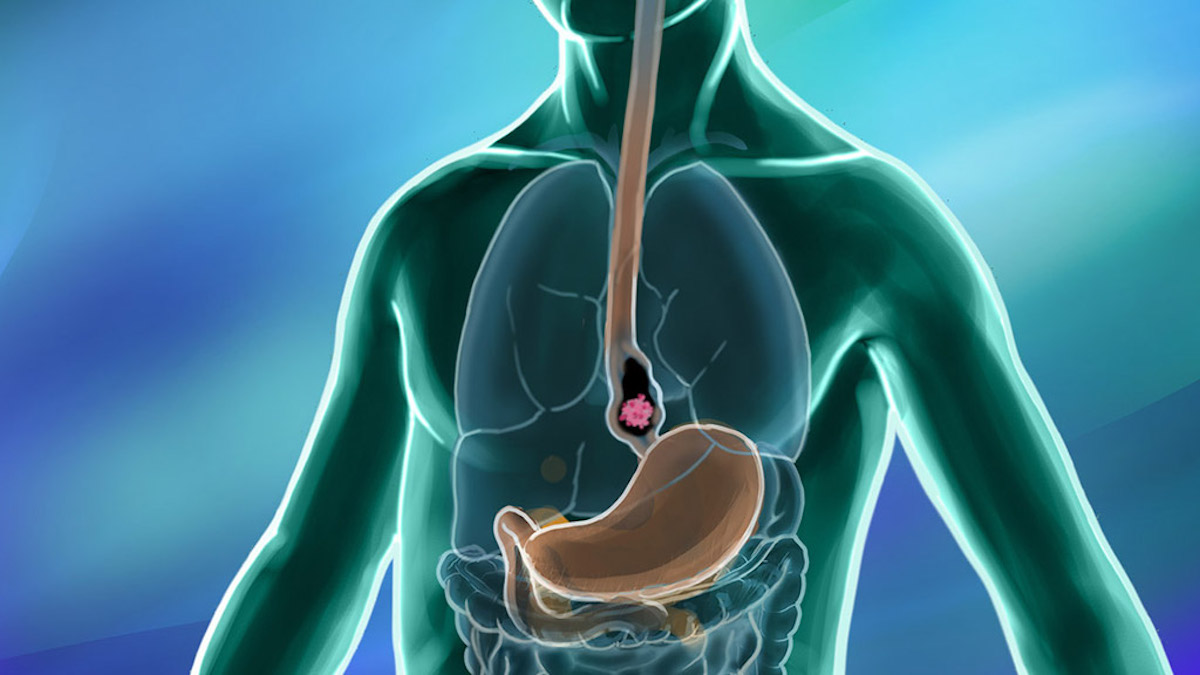
Esophageal cancer is a disease where harmful cells grow in the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that carries food from your mouth down to your stomach. When someone has esophageal cancer, these bad cells multiply in the esophagus, making it hard for the person to swallow food and sometimes causing pain or other problems. This cancer can start in different parts of the esophagus and from different types of cells. Because of this, there are different kinds of esophageal cancer. Some start in the cells that line the inside of the esophagus, while others might start from cells that make mucus.
Are There Different Types?
Esophageal cancer happens when harmful cells grow in the esophagus, the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. There are two main types of this cancer: adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The first type starts in the cells of glands that make mucus in the lower part of the esophagus. It’s more common in some western countries. The second type starts in the flat cells that line the inside of the esophagus. It often occurs in the upper and middle parts and is more common in some parts of Asia and Africa.
Causes of Esophageal Cancer
Several things can increase the risk of this type of cancer. The first one is acid reflux. When stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, it can irritate and damage the lining of the esophagus. This condition is also known as GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease).
Other factors that increase this type of cancer:
- Smoking: using tobacco is a big risk factor. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage the cells in the esophagus, making cancer more likely.
- Alcohol: drinking a lot of alcohol, especially when combined with smoking, increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Barrett’s Esophagus: this is a condition where the cells at the lower end of the esophagus change because of long-term acid reflux. These changes can sometimes turn into cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma.
- Diet: not eating enough fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of this cancer.
- Obesity: being overweight can lead to acid reflux, which in turn can increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
Continue reading on the next page and discover, among others, how you can recognize esophageal cancer and what you should do if you do.

