We’ve all heard about anemia, but did you know there are several types of anemia? A common type is iron deficiency anemia. Less common types are sickle cell anemia and Aplastic Anemia, also called Bone Marrow Failure Syndrome. The latter can be much worse than other anemia types, but is fortunately rare. Aplastic anemia is a serious blood disorder that affects the bone marrow. It’s estimated that around 600 to 900 people in the US are diagnosed with this condition each year. As this blood disorder can happen at any age, it’s important to know how you can recognize it and how someone diagnosed with this can manage the disease.
What is Aplastic Anemia?
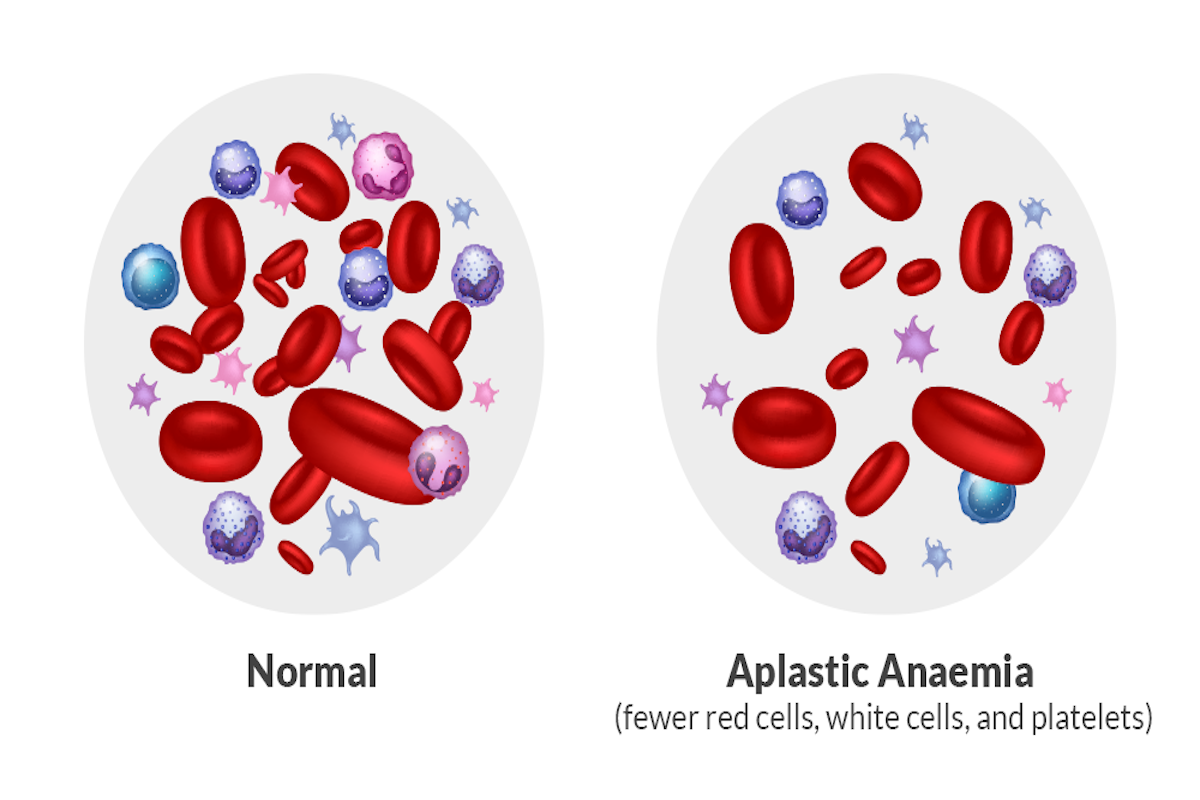
Aplastic anemia is a type of bone marrow failure syndrome that occurs when the bone marrow fails to produce enough red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Without enough blood cells, the body cannot function properly, and this can lead to serious complications.
Causes of Aplastic Anemia
The exact cause of bone marrow failure syndrome is not always known. However, it’s believed to be an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the bone marrow cells. Other possible causes include exposure to certain chemicals, drugs, or radiation, as well as viral infections such as hepatitis or HIV.
Who’s At Risk?
Aplastic anemia can affect anyone, but some people are more at risk than others. These include people who have received radiation therapy or chemotherapy, those with autoimmune disorders such as lupus, and those who have been exposed to certain chemicals or toxins.
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
The symptoms can vary from person to person, which can make it hard for someone to recognize the disorder. Symptoms may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Increased risk of infections
- Unexplained bleeding or bruising
Recognize these symptoms, and make sure to contact your healthcare provider quickly, to know if you suffer from (aplastic) anemia or another blood disorder.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Aplastic anemia is diagnosed through blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy. Blood tests can reveal low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, while a bone marrow biopsy can confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the condition.
Complications of aplastic anemia can include various infections, such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. Which people with this condition may be more susceptible to due to low white blood cell counts. Additionally, people with bone marrow failure syndrome may have a higher risk of developing certain cancers, including leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, or solid tumors like lung or liver cancer. However, it’s important to note that not all individuals with this type of anemia will develop these complications.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
Treatment options for the type of blood disorder may include blood transfusions, medications to stimulate the bone marrow’s production of blood cells, and in severe cases, a bone marrow transplant. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
Make sure to contact your professional healthcare provider when you suspect you’re suffering from any type of anemia. The right treatment can really help you feel/get better. For more information on this condition and possible treatment options, continue your online search here:

