Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) can lead to a range of complications, from less severe to life-threatening. In less severe cases, GVHD might cause issues like skin rashes or digestive problems that, while uncomfortable, can be managed with medical care. However, in more serious instances, GVHD can affect vital organs like the liver and lungs, potentially leading to severe damage or failure. These complications can significantly impact a person’s overall health and quality of life, sometimes becoming life-threatening if not properly managed.
Symptoms Of Graft-versus-host Disease
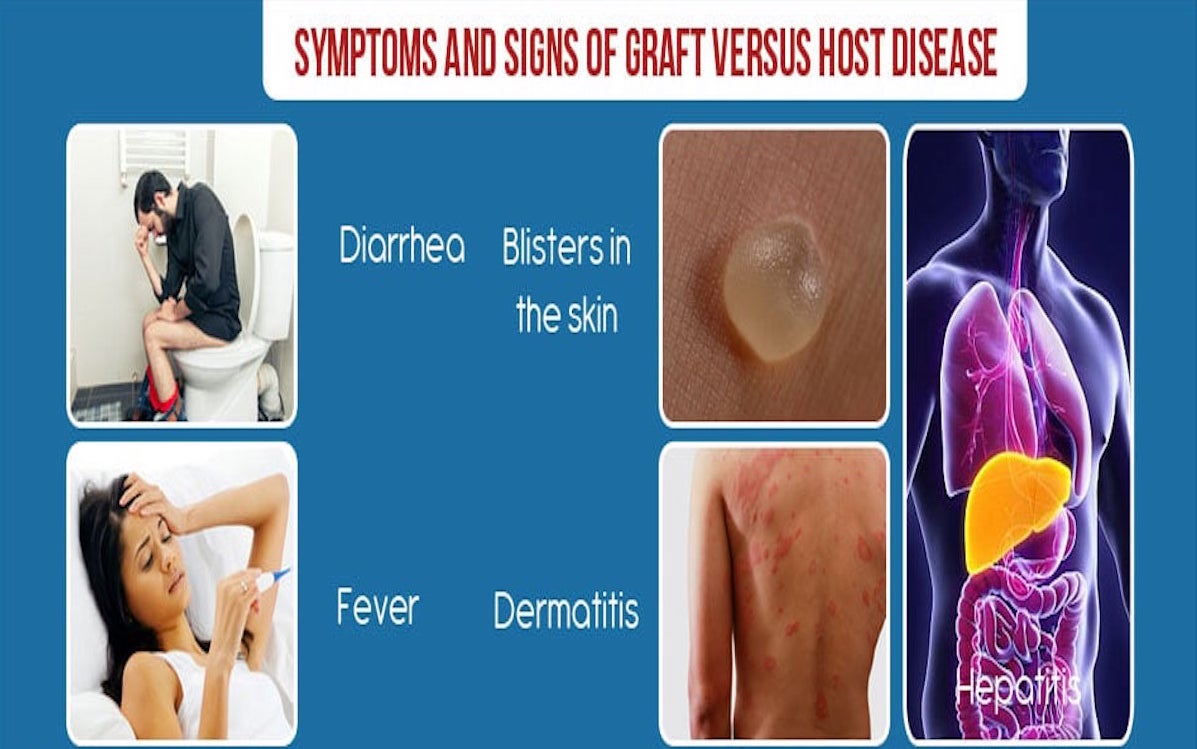
The two most common symptoms of Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) are skin rashes and digestive problems. Skin rashes can appear as red, itchy patches or blisters, often spreading across the body. Digestive problems might include nausea, diarrhea, or stomach pain, making it difficult to eat and absorb nutrients. Other common symptoms of GVHD can include:
- Dry eyes
- Mouth sores
- Liver issues
- Lung problems
Treatment Options for GVHD
Graft-versus-host Disease (GVHD) is diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and biopsies, where a small sample of tissue is taken for examination. Doctors look for signs of GVHD in organs like the skin, liver, and digestive system.
The two most common treatment options for GVHD are corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs. Corticosteroids help reduce inflammation and control the immune response. Immunosuppressive drugs work by weakening the donor’s immune cells that are attacking the recipient’s body. Other common treatments can include using medications to manage symptoms, physical therapy, and supportive care to help with overall well-being.
Need more information? Continue your online search about Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) here:

