Vitamin D deficiency is a common deficiency in the United States, which can lead to problems with bones and muscles. Approximately 50% of Americans are deficient in vitamins A, C, and magnesium. About 50% of the overall population is deficient in vitamin D, regardless of age. This figure is even higher among Americans of color, with around 90% being deficient in vitamin D. Elderly Americans also have a high prevalence of this vitamin deficiency, with approximately 70% being deficient in this vitamin. Fortunately, it’s preventable and treatable, but first, you must learn how you can recognize it.
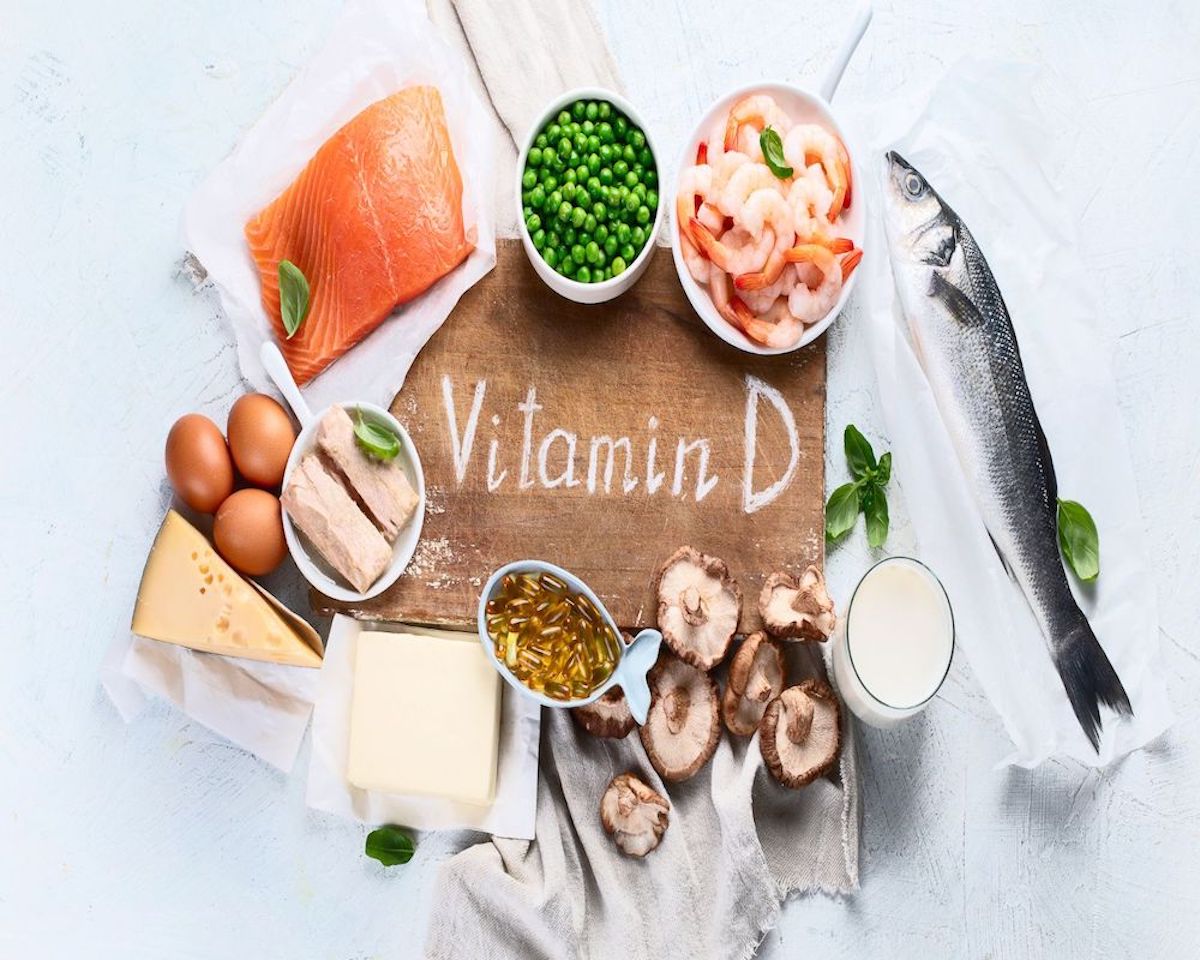

What Is Vitamin D Deficiency &Why Is It Important?
Vitamin D deficiency occurs when there is not enough vitamin D in the body. This deficiency can lead to problems with bone and muscle health. Vitamin D is an important vitamin that plays a role in various body systems, including the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and immune system. There are several ways to get vitamin D, including sunlight exposure, dietary intake, and supplements.
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that helps the body maintain healthy bones and tissues. It is necessary for regulating calcium levels in the blood and bones, and it helps the body absorb and use calcium and phosphorus to build and maintain strong bones. Chronic or severe vitamin D deficiency can lead to reduced absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the intestines, which can cause low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia). The body may try to compensate for this deficiency by increasing the activity of the parathyroid glands, a condition known as secondary hyperparathyroidism. This is the body’s attempt to maintain normal blood calcium levels.
Cause of Vitamin D Deficiency
There are several reasons why someone develops this type of vitamin deficiency. Causes include:
- You don’t consume the recommended levels of the vitamin over time
- Your exposure to sunlight is limited.
- You have dark skin
- Your kidneys cannot convert vitamin D to its active form
- Your digestive tract cannot adequately absorb vitamin D
- You’re obese
- You take medication that has vitamin D deficiency as a side effect
- You underwent weight loss surgery
The big question is: how much vitamin D do I need each day? Well, this varies on your age. Newborns – up to 12 months old need 400 international units (IU), and children from 1-year-old up to 70-year-old adults need 700 IU. The amount for adults older than 71 is 800 IU. In case you have an increased risk, this amount should be even higher. The amount of vitamin D a pregnant woman or woman who breastfeeds should take is 600 IU as well. Possible complications are hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, rickets, and osteomalacia. Untreated vitamin D deficiency can cause long-term bone damage, which is why it’s important to recognize the condition.
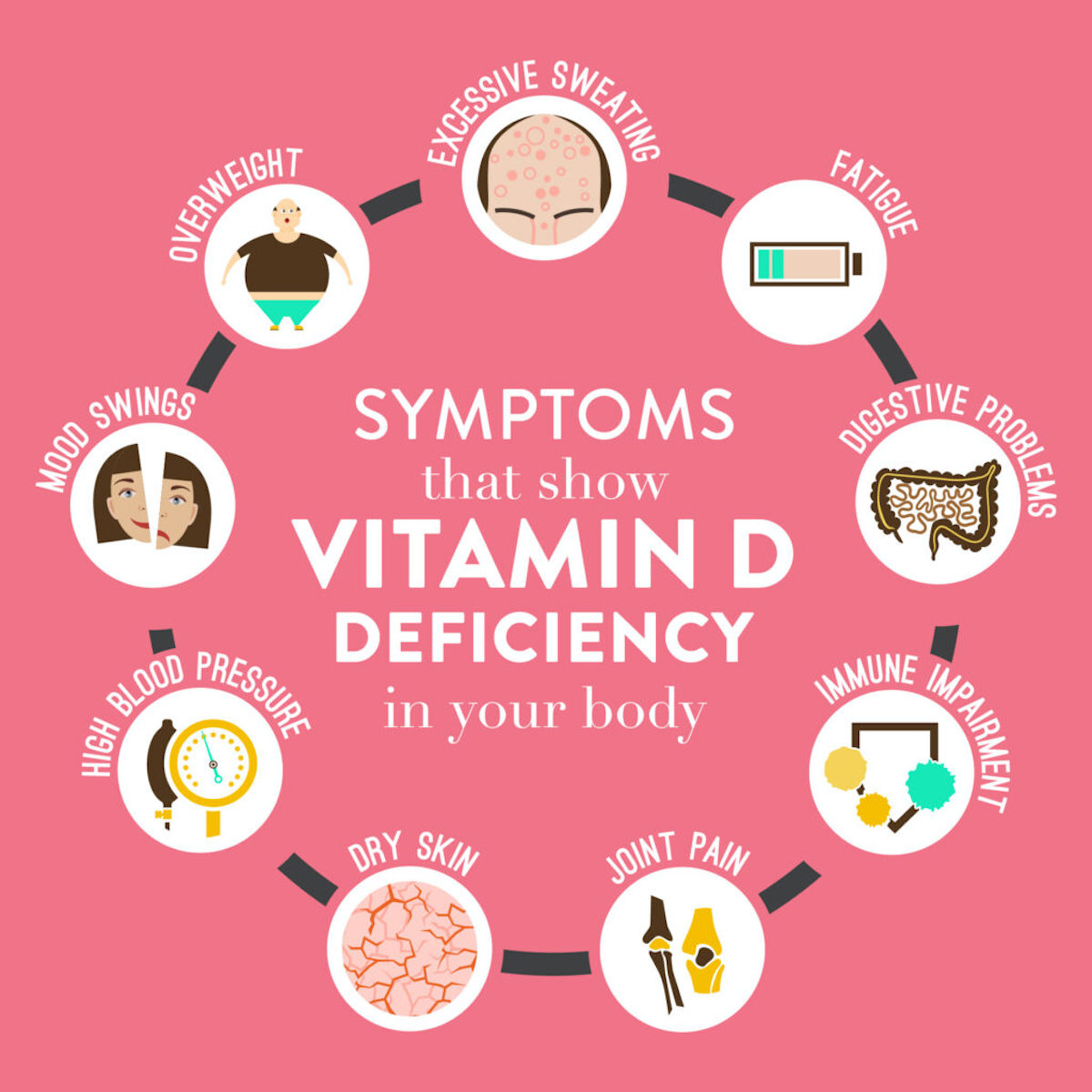
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
A deficiency of vitamin D in children can cause a condition called rickets, which is characterized by abnormal growth patterns and deformities in the bones and joints. Symptoms of rickets may include
- Bent or bowed bones
- Muscle weakness
- Bone pain
- Joint deformities
While rickets is rare, children with mild vitamin D deficiency may experience weak, sore, or painful muscles. Children need to get enough vitamin D to support healthy growth and development. Other symptoms – for adults and children – include:
- Fatigue
- Bone pain
- Muscle weakness, muscle aches or muscle cramps
- Mood changes, like depression.
- Hair loss
- Loss of appetite
- Pale skin
Treatment Options for Vitamin Deficiencies
The main goal of treatment and prevention for vitamin D deficiency is to achieve and maintain a good level of vitamin D in the body. To achieve this, it is important to consume vitamin D-rich foods, get adequate sunlight exposure, and consider taking vitamin D supplements as needed. Vitamin D supplements come in two forms: D2 and D3. Examples of vitamin d-rich foods are fatty fish, like salmon, mushrooms, cheese, and egg yolks.
Anyone can get vitamin D deficiency, even infants and children, and it can cause serious medical conditions. Which is why it’s vital to stay informed about vitamin deficiencies. Continue your online search about vitamin D – or other – deficiencies, which foods you should and shouldn’t eat, and other possible treatment options here:

