Approximately 50 million Americans suffer from a ringing in their ear that no one else can hear, but affects their lives daily. This problem is called tinnitus and is a symptom that may develop when someone suffers from an underlying condition. A severe form of the condition can affect someone’s daily life, they cannot work, and there are several cases of people developing depression or anxiety due to the constant ringing in their ears. Contacting your professional healthcare provider and getting the right diagnosis is vital because it can cause serious complications for your physical and mental health.
Causes of Tinnitus
In many cases, an exact cause for tinnitus is never found, but researchers did find multiple reasons that can cause or worsen this problem. Often it is a case of age-related hearing loss or being regularly exposed to loud sounds. Tiny hair cells in your ear normally move when your ear receives sound (waves). If these hairs are damaged or broken – what can happen due to aging or being exposed to loud sounds, they can leak electrical impulses to the brain, which causes tinnitus. Other common causes are:
- Ear infection or blockage in the ear canal.
- Head or neck trauma
- Medication, like NSAIDs or certain antibiotics
It can also be caused by medical conditions or infections that affect the nerves in the ear and the hearing center of the brain. It is less common but the causes include:
- Meniere’s disease
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Otosclerosis in ear bones
- Muscle spasms in the inner ear
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- Acoustic neuroma or other head/neck tumors
- Blood vessel disorders, like high blood pressure or atherosclerosis
- Chronic conditions, like diabetes, migraine, rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
Anyone can get tinnitus, but there are some factors that can increase the risk. These include regularly exposing yourself to loud sounds and getting older. Your gender also plays a role; men, for example, are more likely to have the condition. In addition, alcohol drinkers, smokers, and people with heart problems also have an increased risk. If you suspect you’re suffering from tinnitus, it’s important to contact your professional healthcare provider, because tinnitus can have big complications, like sleep problems, depression, and serious headaches.
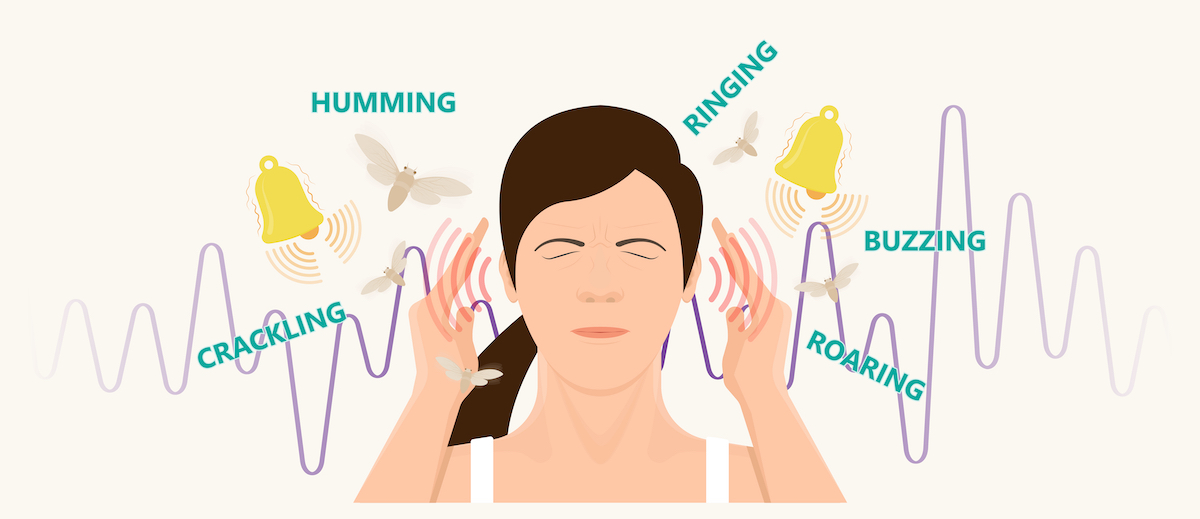
Symptoms of Tinnitus
Often, tinnitus is described as a ringing in the ears even though no one else can hear it or there is no external sound present. This ringing can also be:
- Buzzing
- Roaring
- Clicking
- Hissing
- Humming
This phantom noise can be constant, but there are also many cases of the noise coming and going. In addition, tinnitus can affect one or both ears. The noise can be so loud that it interferes with your ability to concentrate or hear something else.
Are There Treatment Options?
To start with the more unfortunate news: there is no cure for tinnitus, but don’t panic! After some severe testing and getting the right diagnosis, there are ways to treat the (constant) ringing in the ear(s). Testing for tinnitus consists of a physical examination, a hearing test, imaging, like CT or MRI scans, and a blood test to rule out other medical conditions, like anemia, thyroid problems, or vitamin deficiencies. Once the diagnosis of tinnitus is made, treatment options include:
- Earwax removal, to reduce symptoms
- Treating possible underlying conditions
- Hearing aids
- Change of medication
- Noise suppression, like white noise machines & masking devices
- Counseling, like tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) & cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Prescribed medication, to reduce symptoms and prevent complications
As there is no cure for tinnitus, it’s very important to treat and manage the symptoms of this health problem. Make sure to contact your professional healthcare provider when you suspect you’re suffering from this! The right treatment can really help you feel better. For more information on this ear condition and possible treatment options, continue your online search here:

