Plaque psoriasis is a common skin condition that affects approximately 7.5 million people in the United States. It is one of the most common skin conditions in the country, affecting individuals of all ages and ethnicities. While it’s not contagious, it can impact a person’s self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding this condition is essential to managing it effectively. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of plaque psoriasis to help you gain a better understanding of what it is and how it can affect you.
What Causes Plaque Psoriasis?
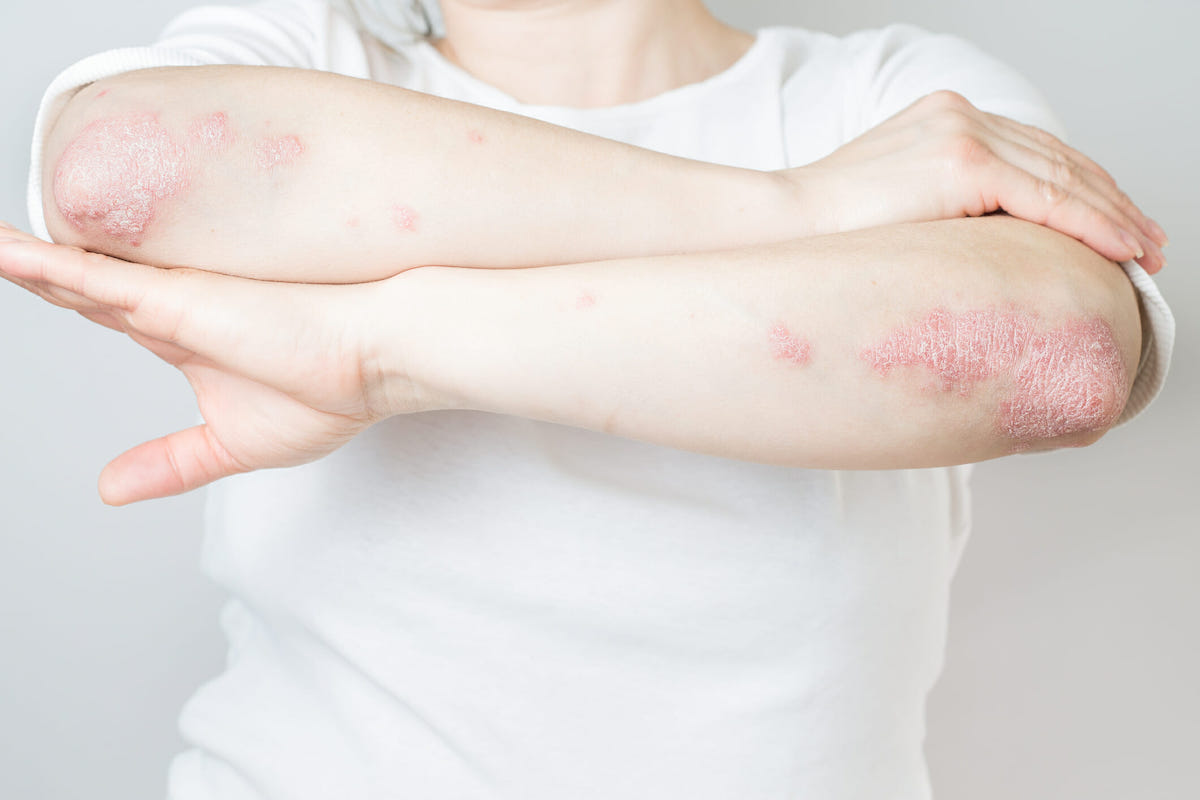
Plaque psoriasis, a common skin disorder, is an autoimmune condition. While the exact cause is not fully understood, medical experts believe it is influenced by genetic and immune system factors. In simple terms, certain genes increase the likelihood of developing psoriasis. When triggered, the immune system becomes overactive and attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid growth and plaque formation. It’s important to clarify that plaque psoriasis is not a result of poor hygiene or personal fault.
Are There Any Triggers?
As read in the previous paragraph, plaque psoriasis gets triggered. These triggers can vary from person to person. Some common factors that can trigger or worsen plaque psoriasis:
- Stress: emotional or physical stress can lead to flare-ups or make existing symptoms worse.
- Infections: certain infections, like strep throat or respiratory infections, can trigger psoriasis or cause it to worsen.
- Injury to the skin: any injury to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or sunburns, can trigger a psoriasis outbreak in that area.
- Medications: certain medications, such as beta-blockers, lithium, or antimalarial drugs, have been associated with triggering or aggravating psoriasis symptoms.
- Climate & weather: cold and dry weather conditions may cause flare-ups, while warm and humid climates may provide relief for some individuals.
- Smoking & alcohol: smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of developing psoriasis or worsening existing symptoms.
- Hormonal changes: hormonal changes, such as during puberty or pregnancy, can influence the severity of psoriasis.
Continue reading on the next page and, discover among others, how you can recognize this skin condition.

