Parkinson’s disease is a common and progressive brain disorder that affects many people around the world. In the United States, about 60,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. Although we don’t know exactly why it happens, some things can increase the chances of getting Parkinson’s disease. These include getting older, having a family history of the disease, and being exposed to certain harmful substances in the environment. In this article, we will explain the causes, symptoms, and treatments for Parkinson’s disease. Whether you are someone with the disease, a caregiver, or just curious to learn more, this information will be helpful to you.

Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
The exact causes of Parkinson’s disease are not completely known. However, scientists believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a role. Some people may have certain genes that increase their chances of developing the disease. Additionally, exposure to certain environmental factors, like toxins or chemicals, might also contribute to the development of Parkinson’s in some individuals. While more research is needed to fully understand the causes, these factors are believed to be involved in the development of the condition.
Types of Parkinson’s Disease
Information about the different types of Parkinson’s disease can be overwhelming. To make it easier to understand, we’ve created this table which explains which types of Parkinson’s disease there are and what their prevalence is.
| Parkinson's Disease Types | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease | The most common type of Parkinson's disease, with no known specific cause. | The most prevalent type; affects the majority of cases |
| Parkinson's Disease with Lewy Bodies | Characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain, which can lead to both movement and cognitive problems. | Accounts for approximately 10-15% of cases |
| Parkinson's Disease due to Genetic Mutations | Caused by specific genetic mutations inherited from family members. These genetic changes increase the risk of developing the condition. | Accounts for a small percentage of cases |
| Parkinsonism-Plus Syndromes | A group of disorders with symptoms similar to Parkinson's disease but with additional features. Examples include multiple system atrophy (MSA) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). These conditions may have distinct underlying causes and may progress differently from idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Relatively rare; accounts for a small percentage |
| Drug-Induced Parkinson's Disease | Parkinsonism symptoms are caused by certain medications or drugs, appearing as a side effect. Symptoms usually improve or resolve once the medication is stopped. | Relatively rare; varies based on medication use |
| Secondary Parkinsonism | Parkinsonism symptoms are caused by other underlying conditions or factors such as head trauma, brain infections, or exposure to toxins. Symptoms improve or resolve once the underlying cause is treated or removed. | Varies depending on the underlying condition/cause |
Parkinson’s disease can lead to various complications. Some non-serious complications include problems with movement, such as tremors, stiffness, and slowness. People with Parkinson’s may also experience difficulties with balance, causing them to be at a higher risk of falls. Other non-serious complications can include sleep problems, mood changes like depression or anxiety, and constipation. On the other hand, there are more serious and potentially life-threatening complications, such as swallowing difficulties that may lead to choking or aspiration pneumonia, as well as a higher risk of developing dementia or experiencing hallucinations. This is why it’s vital to recognize the condition’s symptoms.
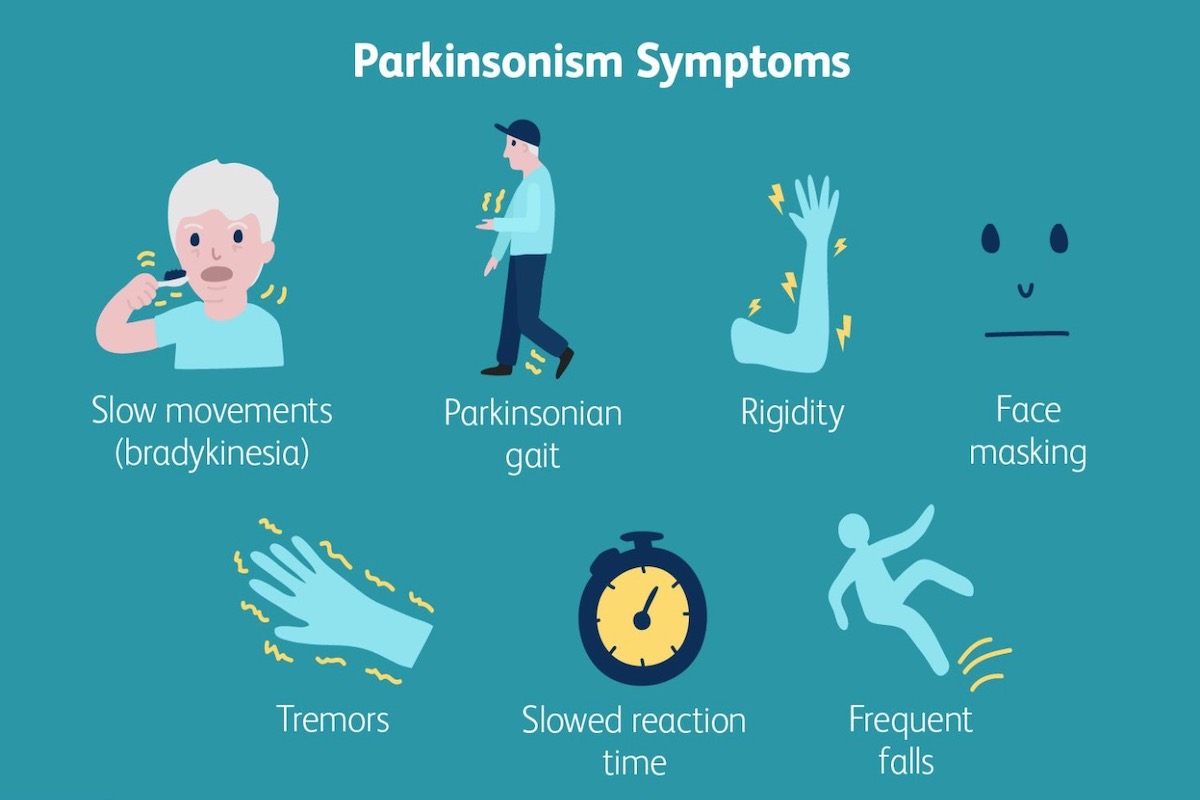
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a condition that causes various symptoms related to movement and other aspects of the body. Two of the most common symptoms are tremors and stiffness. Tremors are uncontrollable shaking or trembling, usually in the hands, arms, legs, or jaw. This can make it difficult to perform tasks requiring fine motor skills, like writing or holding objects. Stiffness refers to muscle rigidity, which can make movements slow and difficult, causing a feeling of stiffness or tightness in the body. Other symptoms may include:
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement and difficulty initiating movements.
- Postural instability: Problems with balance and coordination, leading to unsteadiness and an increased risk of falls.
- Akinesia: Difficulty initiating voluntary movements.
- Masked face: Reduced facial expressions, resulting in a blank or emotionless appearance.
- Micrographia: Small, cramped handwriting.
- Voice and speech changes: Softening of the voice, slurred speech, or monotone speech.
- Freezing of gait: A sudden inability to start or continue walking.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy.
- Sleep disturbances: Trouble sleeping, vivid dreams, or daytime sleepiness.
- Depression and anxiety: Feelings of sadness, low mood, and worry.
- Cognitive changes: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and changes in thinking abilities.
Are There Any Treatment Options?
Unfortunately, until this day, there is no cure for Parkinson’s. However, there are several treatment options to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life. The primary approach to treatment involves medications that help regulate the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine, which is essential for movement control. These medications can help reduce tremors, stiffness, and other motor symptoms.
In some cases, deep brain stimulation (DBS) may be recommended, which involves placing electrodes in specific areas of the brain to help control abnormal electrical signals and manage symptoms. Additionally, physical therapy and exercises can help improve strength, balance, and flexibility. Occupational therapy can assist with adapting daily activities to make them easier to perform. Speech therapy can target voice and speech changes.
We know also, it can be a challenging problem to deal with, but there are solutions available. Identifying the cause and seeking the right treatment for your situation is important. We hope this article has provided helpful information on how to deal with Parkinson’s. For more info on this topic, or other brain problems, start your search here:

