Receiving a diagnosis of ovarian cancer is a nightmare for most patients. After times of uncertainty, you finally know what it is, but for most diagnosed patients, it is just the beginning of more uncertain times. After the diagnosis, you’ll get more and more tests, and, if possible, you’ve to start treatment immediately. Ovarian cancer is a serious health issue, but it’s not as common as some other types of cancer in the United States. Still, it’s a big concern for women. Almost every year there are about 20,000 new cases, and around 13,500 people died from it.
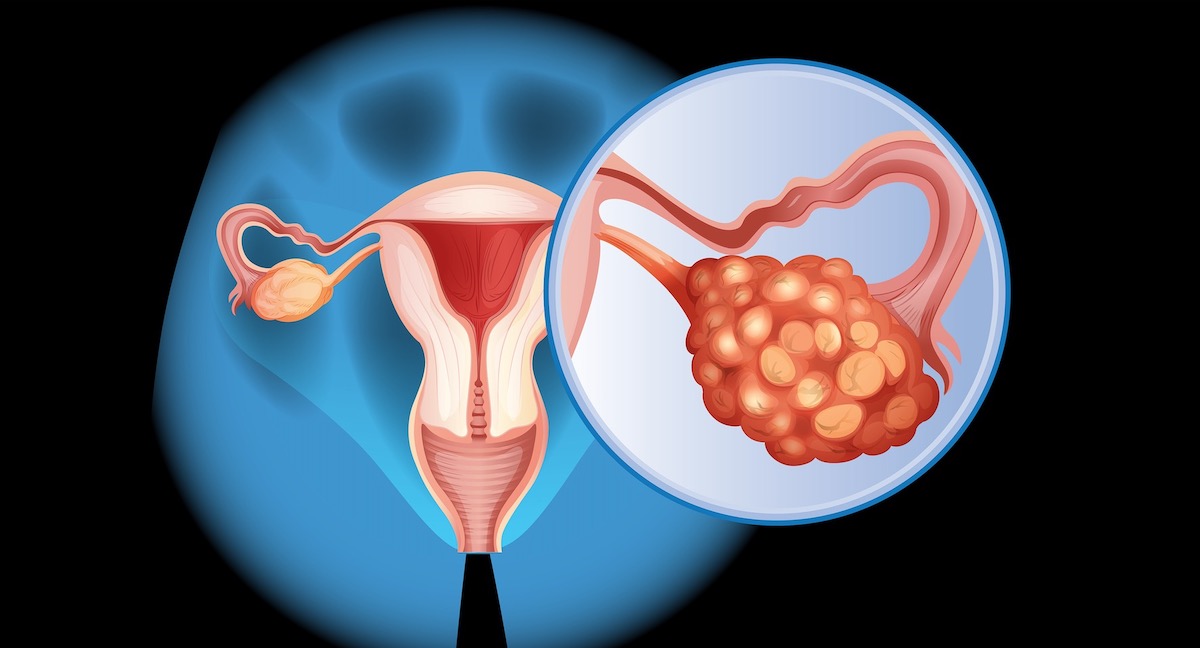
What Is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in a woman’s ovaries, which are small, almond-sized organs located in the lower abdomen. The ovaries have a crucial role in the female reproductive system. They produce eggs and also release hormones like estrogen and progesterone. There are different types, and they can behave differently. To make it easier to understand we’ve put them in the following overview:
| Type of Ovarian Cancer | Description |
|---|---|
| Epithelial Ovarian Cancer | This is the most common type, originating in the tissue covering the ovaries. It includes several subtypes, such as serous, endometrioid, clear cell, and mucinous ovarian cancer. |
| Germ Cell Tumors | These cancers develop from the egg-producing cells within the ovaries. Germ cell tumors are less common than epithelial ovarian cancer and often affect younger women. |
| Stromal Tumors | Stromal tumors begin in the hormone-producing cells of the ovary, which help regulate female hormones like estrogen and progesterone. These tumors are rare and can cause hormonal imbalances. |
How Is This Type of Cancer Caused?
This type of cancer typically starts when normal cells in the ovaries undergo genetic changes, causing them to grow and divide uncontrollably. These abnormal cells can form tumors within the ovaries. Ovarian cancer is a complex disease, and its exact cause isn’t always clear.
A woman’s risk of ovarian cancer increases with age, family history of the disease (especially with genetic mutations like BRCA1 or BRCA2), personal history of certain cancers, never having been pregnant, endometriosis, long-term estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT) use after menopause, and, potentially, genital talcum powder use. Keep in mind, having these risk factors doesn’t guarantee this type of cancer, and many diagnosed with it have none. That’s why it’s so important to know how you can recognize the cancer.
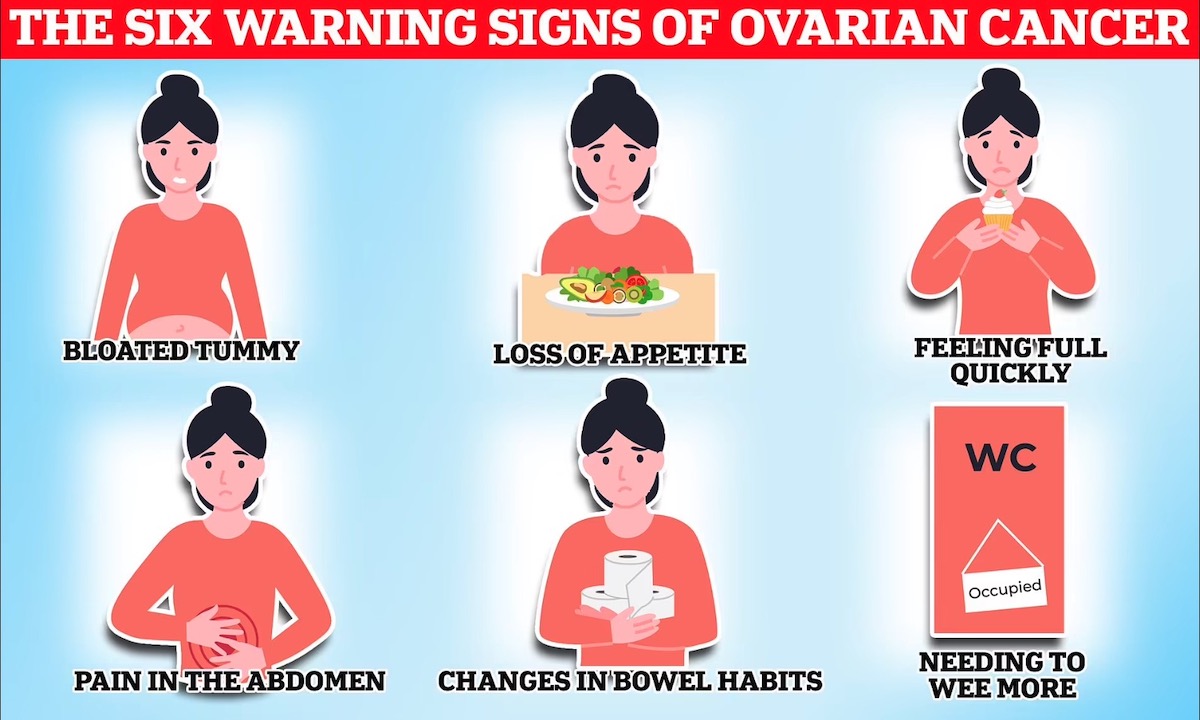
How Can I Recognize Ovarian Cancer?
One of the most common early signs of ovarian cancer is a feeling of fullness or bloating in the lower abdomen that doesn’t go away. This bloating may be different from the occasional bloating many people experience and may last for several weeks. Another common symptom is pelvic pain or pressure. Ovarian cancer can cause discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the lower pelvis or abdomen. This pain may be ongoing or occur more frequently than usual. Other possible symptoms include:
- Difficulty eating: women with ovarian cancer may have a reduced appetite or find it uncomfortable to eat, leading to unintended weight loss.
- Frequent urination: needing to urinate more often than usual, even if there’s not much urine to pass.
- Changes in bowel habits: ovarian cancer can affect the digestive system, leading to constipation or other changes in bowel habits.
- Fatigue: feeling unusually tired or having low energy levels, even after getting enough rest.
- Back pain: Some women with ovarian cancer may experience pain in the lower back.
- Abnormal menstrual bleeding: Changes in menstrual patterns, such as heavier or irregular periods, can sometimes be a sign.
- Pain during sexual intercourse: Pain or discomfort during sexual activity can also be a symptom.
Complications of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer can result in complications such as metastasis, infertility, bowel or bladder problems, malnutrition, ascites, blood clots, secondary cancers, emotional distress, and treatment side effects. However, the severity and occurrence of these complications can vary.
Ovarian cancer is often referred to as the “silent killer” due to its subtle symptoms and challenges in early detection. Its late-stage diagnosis, when the cancer has already advanced, can make it exceptionally challenging to treat effectively. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available screening methods is crucial in combating this formidable disease and improving outcomes for those affected.
What Are the Stages of Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer can be classified into four stages, each with its own characteristics and implications for survival. Understanding these stages, their associated survival rates, and common symptoms is vital for early detection and appropriate treatment. To make it easier to understand we’ve created the following overview:
| Stage | Subcategory | Description | Survival Rate | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I | IA | Cancer is limited to one ovary. | About 90% | Often no symptoms, or mild abdominal discomfort. |
| IB | Cancer involves both ovaries. | About 90% | Often no symptoms, or mild abdominal discomfort. | |
| IC | Cancer is present in one or both ovaries, with tumor rupture, capsule rupture, or malignant cells on the ovary surface. | About 90% | Often no symptoms, or mild abdominal discomfort. | |
| Stage II | IIA | Cancer has spread to other pelvic organs. | Around 70-90% | Pelvic pain, bloating, frequent urination. |
| IIB | Cancer involves one or both ovaries, with tumor capsule rupture or malignant cells on the ovary surface. | Around 70-90% | Pelvic pain, bloating, frequent urination. | |
| Stage III | IIIA | Cancer has spread to the abdominal lining or lymph nodes in the abdomen. | About 39-70% | Digestive problems, weight loss, ascites (abdominal fluid). |
| IIIB | Cancer has spread to the abdominal lining, with tumor implants on the small bowel or omentum. | About 39-70% | Digestive problems, weight loss, ascites (abdominal fluid). | |
| IIIC | Cancer involves lymph nodes in the abdomen or retroperitoneal (behind the abdominal) lymph nodes, or there are microscopic deposits of cancer in the abdomen. | About 39-70% | Digestive problems, weight loss, ascites (abdominal fluid). | |
| Stage IV | IVA | Cancer has spread to distant organs outside the abdomen or pelvic area. | About 17-34% | Severe abdominal pain, breathlessness, extreme fatigue. |
| IVB | Cancer involves pleural fluid, a collection of fluid around the lungs. | About 17-34% | Severe abdominal pain, breathlessness, extreme fatigue. |
How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
Ovarian cancer is diagnosed through several steps: First, someone notices unusual signs like persistent bloating or abdominal pain and sees a doctor who asks about their symptoms. The doctor then does a physical exam and may order imaging tests like ultrasound or blood tests to check for specific markers linked to ovarian cancer. If cancer is suspected, a tiny piece of tissue may be taken from the ovary to confirm the diagnosis.
Are There Treatment Options?
Fortunately, there are treatment options for ovarian cancer. The choice of treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer and the person’s overall health. Options include:
- Surgery: doctors often start by removing the cancerous tissue through surgery. Sometimes, they remove one or both ovaries, the uterus, and nearby tissues. This helps stop the cancer from spreading.
- Chemotherapy: after surgery, many people receive chemotherapy, which is medicine that kills cancer cells. It’s usually given in cycles and can be given through pills or injected into a vein.
- Radiation: in some cases, radiation therapy may be used to target and kill cancer cells with high-energy rays. But it’s not as common for ovarian cancer as surgery and chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapy: this is a more specialized treatment that targets specific molecules involved in cancer growth. It’s often used when other treatments haven’t worked.
These days, medical professionals have various ways to treat cancer, including the options mentioned above. Sometimes, doctors combine these treatments, but there may be cases where they are no longer effective, prompting consideration of other options. To stay informed about new treatments, it is crucial to conduct extensive online research. If you are diagnosed with ovarian cancer and unsatisfied with your treatment plan, seeking a second opinion from another hospital or oncology center is always a wise decision. Keep exploring to learn more about cancer and its treatment options. Continue your search here:

