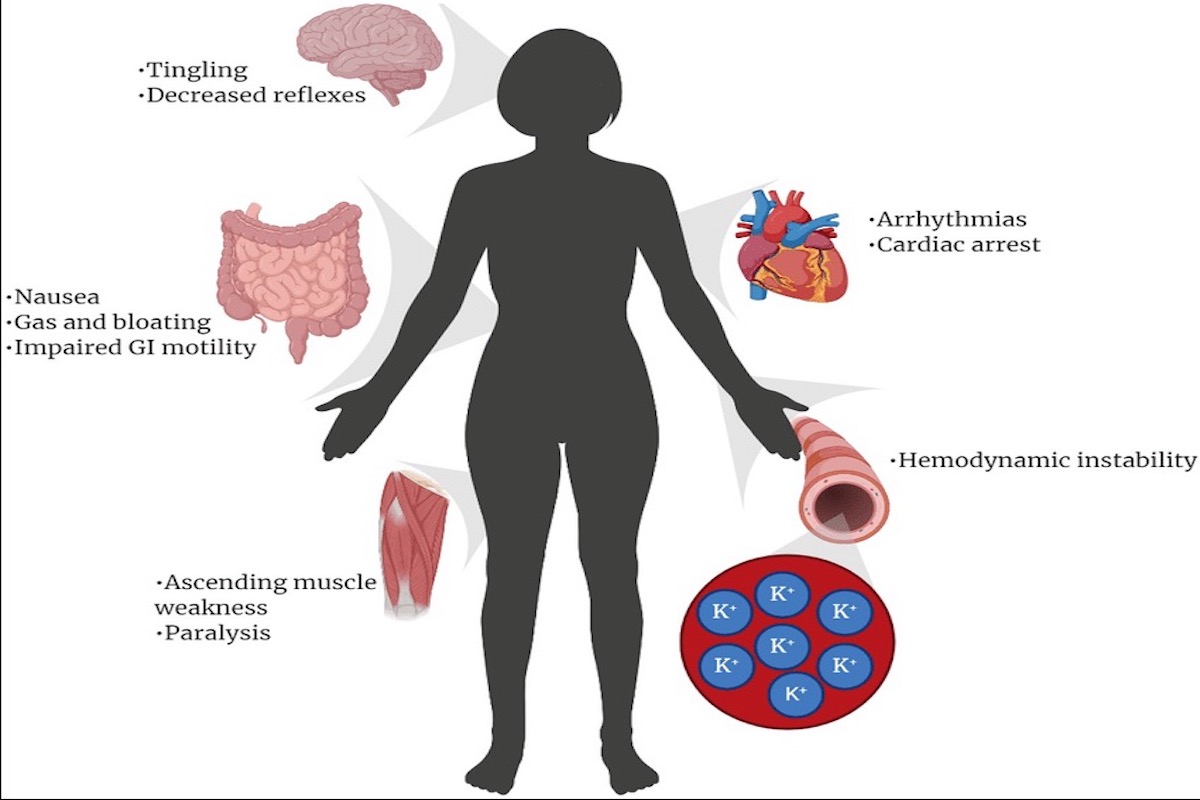
Hyperkalemia can lead to several complications. These include problems with the heartbeat, such as irregular rhythms or a slower heartbeat. It can also cause muscle weakness, nausea, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, hyperkalemia can even lead to cardiac arrest, which is when the heart stops working.
Symptoms of High Potassium Levels
Having high potassium levels in your blood, may not always cause noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can vary depending on the severity of the condition. The most common symptom is an irregular heartbeat or palpitations. This can manifest as a faster heart rate, skipped beats, or an abnormal rhythm. Other symptoms, include:
- Muscle weakness or numbness
- Fatigue or tiredness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breathing difficulties
Treatment Options for Hyperkalemia
The treatment options for hyperkalemia depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications that help lower potassium levels or improve its elimination from the body. Examples include potassium binders, diuretics, or medications that enhance potassium excretion by the kidneys.
- Dietary changes: Modifying your diet can play a role in managing hyperkalemia. This may involve reducing potassium-rich foods like bananas, oranges, tomatoes, potatoes, and salt substitutes. Consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help create a suitable meal plan.
- Intravenous therapy: In severe cases or when immediate correction is required, intravenous administration of medications like calcium gluconate or sodium bicarbonate may be necessary to stabilize the heart’s electrical activity.
- Hemodialysis: For individuals with kidney failure or life-threatening hyperkalemia, hemodialysis may be recommended. This procedure filters the blood to remove excess potassium and other waste products.
Is Hyperkalemia Preventable?
In some cases, it can be preventable by taking certain measures. Here are some steps that can help reduce the risk of developing hyperkalemia:
Follow a balanced diet:
Maintain a healthy, balanced diet that includes moderate amounts of potassium-rich foods. Be mindful of consuming excessive amounts of potassium, especially if you have a condition that increases your risk of hyperkalemia.
Stay hydrated:
Drink an adequate amount of fluids to support kidney function and promote proper potassium balance in the body.
Follow medication instructions:
Take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider and inform them about all the medications you are currently taking. Some medications can increase potassium levels, so it’s crucial to be aware of potential interactions or side effects.
By following these tips, you may be able to help prevent or manage the condition. We know, it can be a challenging problem to deal with, but there are solutions available. It’s important to identify the cause and seek the right treatment for your specific situation. We hope this article has provided helpful information on how to deal with high potassium levels. For more info on this topic, or other tips start your search here:

