Hair loss is a common issue that affects almost everyone at some point in their life, and it’s nothing to worry about. However, it can be a severe problem that causes distress and affects someone’s quality of life. In fact, several studies show that millions of people in the US suffer from severe hair loss. We provide information on what causes (severe) hair loss, how to treat it, and if there are ways to prevent it. If you or someone you know is experiencing this problem, keep reading to learn more.
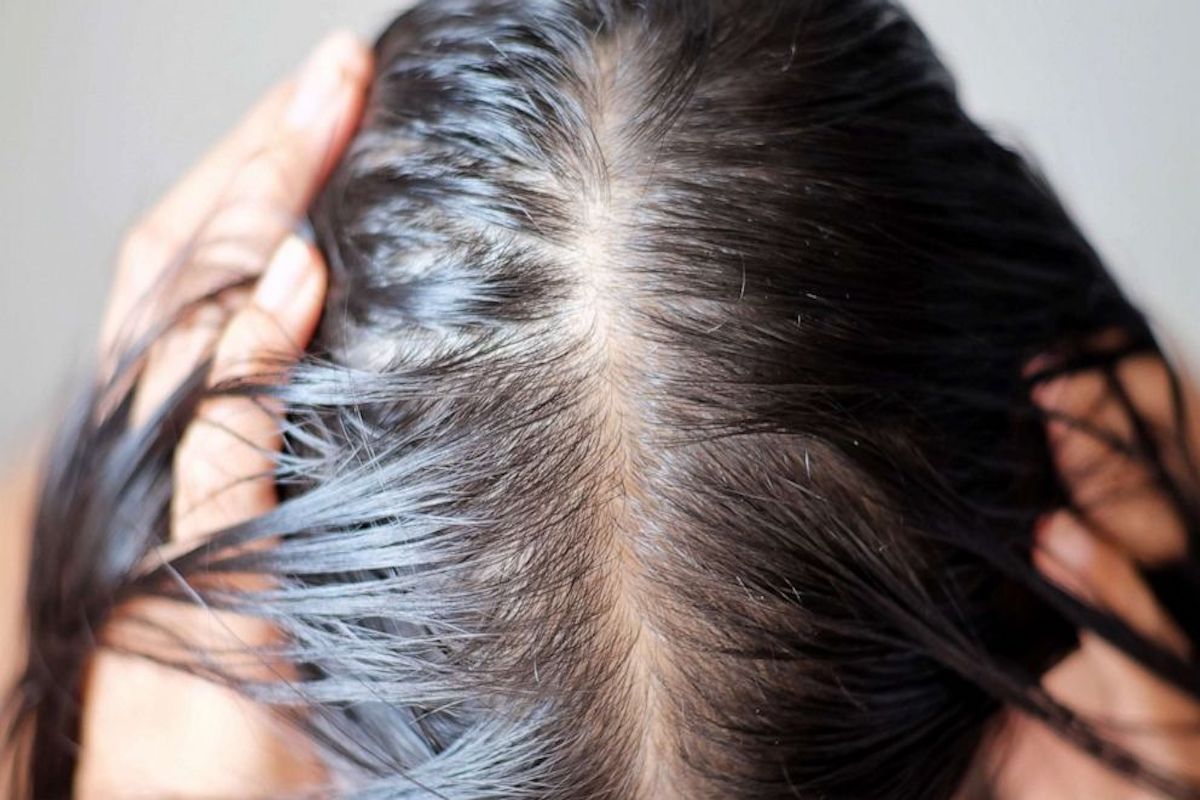

What Is Hair Loss?
Hair loss is a condition where a person starts losing hair from their scalp or other parts of their body. The medical term for this is alopecia. There are different types of hair loss, such as male and female pattern baldness, alopecia areata, and telogen effluvium. These types can vary in severity and the amount of loss of hair they cause. In some cases, the condition can be temporary, while in others it may be permanent. To make it a bit easier to understand we made an overview of the most common hair loss types and what they entail:
| Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Male pattern baldness | The most common type in men, characterized by a receding hairline and hair thinning on the crown of the head |
| Female pattern baldness | The most common type in women, characterized by a widening part and thinning hair |
| Alopecia areata | An autoimmune disorder that causes patchy hair loss on the scalp, face, and other parts of the body |
| Telogen effluvium | A type of temporary hair loss that occurs after a stressful event, illness, or hormonal change |
| Anagen effluvium | A type of hair loss that occurs during the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle, often caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy |
| Traction alopecia | Hair loss caused by constant tension or pulling on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles |
| Scarring alopecia | Hair loss that occurs when hair follicles are destroyed and replaced by scar tissue |
Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, aging, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and nutritional deficiencies. The most common cause is genetics, specifically a condition called androgenetic alopecia, which can cause male or female pattern baldness. This condition occurs when hair follicles shrink over time, producing shorter and thinner hair until they stop growing completely. Other (less) common causes include
- Age
- Hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause
- Medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or alopecia areata
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as iron deficiency anemia or protein deficiency
- Medications or treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Stress or trauma, such as surgery, illness, or emotional stress
- Hairstyles that pull on the hair, such as tight braids or ponytails
- Chemical treatments, such as hair dyes, perms, or relaxers
- Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or scleroderma.
Identifying the underlying cause of hair loss is crucial for finding the appropriate treatment. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the cause and provide the best course of action.
What Are the Symptoms?
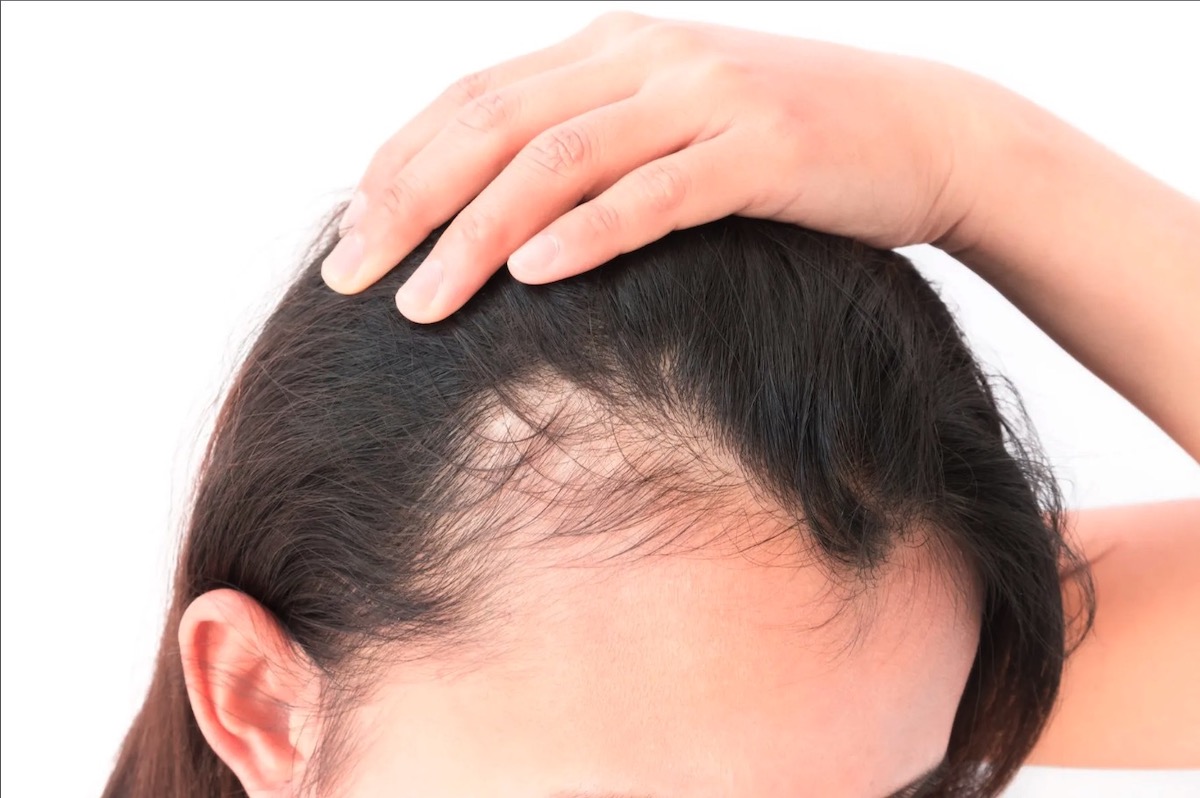
Of course, the most common – and obvious – symptom is losing hair and getting bald sport. However, other symptoms also indicate you’re suffering from (severe) hair loss. Early symptoms may include noticing more hair than usual on your pillow, in your hairbrush, or the shower drain. You may also notice thinning or a widening part in your hairline.
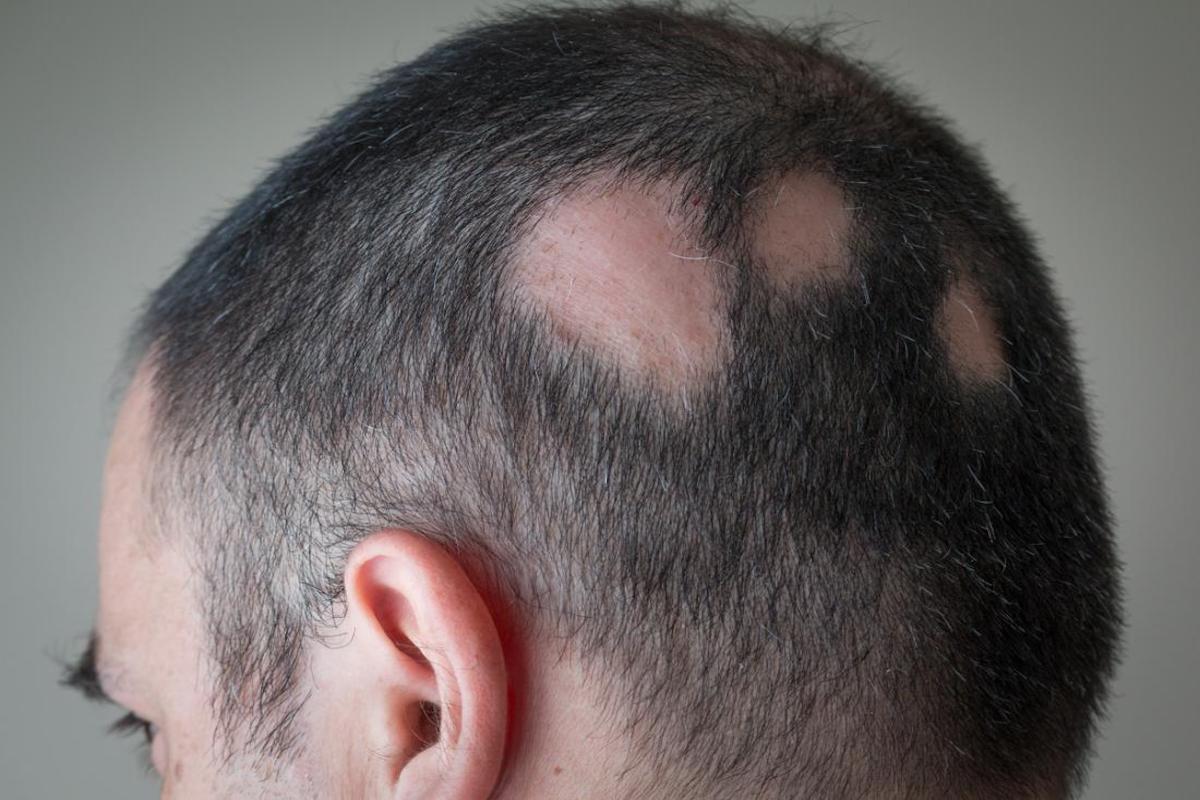
In some cases, it may cause itching or a tingling sensation on the scalp. It’s important to note that everyone loses some hair every day, so it’s not always easy to tell if you’re experiencing hair loss. However, if you notice a significant increase in the amount of hair you’re losing or any changes in your hairline, it may be a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and find appropriate treatment options.
Are There Any Treatment Options?
When a healthcare provider suspects hair loss, they will usually begin by asking about your medical history and performing a physical examination of your scalp and hair. They may also perform blood tests or other diagnostic tests to check for underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the loss of hair. In some cases, a biopsy of the scalp may be necessary. The treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and the individual case of hair loss.
| Causes | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness) | Medications such as minoxidil or finasteride, hair transplant surgery, or wigs/hairpieces |
| Hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause) | No treatment necessary, as hair will usually grow back after hormonal changes have stabilized |
| Medical conditions (such as thyroid disorders or alopecia areata) | Treatment of the underlying medical condition, which may include medications or other medical interventions |
| Nutritional deficiencies (such as iron deficiency anemia or protein deficiency) | Dietary changes or supplements to correct the deficiency |
| Medications or treatments (such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy) | Hair will usually grow back once treatment is complete |
| Stress or trauma (such as surgery, illness, or emotional stress) | No specific treatment necessary, as hair will usually grow back once the stressor has been resolved |
| Hairstyles that pull on the hair (such as tight braids or ponytails) | Avoidance of tight hairstyles and using hair ties that do not pull on the hair |
| Chemical treatments (such as hair dyes, perms, or relaxers) | Avoidance of chemical treatments or using gentler alternatives |
| Autoimmune disorders (such as lupus or scleroderma) | Treatment of the underlying autoimmune disorder, which may include medications or other medical interventions |
The big question of course is: are there ways to prevent it? Well, some types or causes are preventable and some types are not, but you can try to put it off as long as possible. Here are some tips that may help:
Are There Ways to Prevent It?
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a well-balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals can help promote healthy hair growth.
- Avoid tight hairstyles: Hairstyles that pull on the hair, such as tight braids or ponytails, can cause hair loss over time. Opt for looser hairstyles or hair ties that do not pull on the hair.
- Avoid harsh chemicals: Chemical treatments like hair dyes, perms, or relaxers can damage the hair and cause it to break or fall out. Consider gentler alternatives or avoiding chemical treatments altogether.
- Handle hair gently: Brushing or styling hair too aggressively can cause damage and breakage. Handle hair gently and avoid excessive heat styling.
- Manage stress: Stress can contribute to the condition, so finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise or meditation, may help prevent it.
- Seek prompt treatment for medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune disorders, can contribute. Seeking prompt treatment for these conditions may help prevent or manage hair loss.
- Consult with a healthcare provider: If you’re experiencing hair loss, consulting with a healthcare provider can help identify the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment options.
By following these tips, you may be able to help prevent or manage the condition. We know, it can be a challenging problem to deal with, but there are solutions available. It’s important to identify the cause and seek the right treatment for your specific situation. We hope this article has provided helpful information on how to deal with hair loss. For more info on this topic, or hair tips start your search here:

