Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma can lead to both life-threatening and less severe complications. Life-threatening complications include the spread of cancer to major organs like the lungs, or brain, which can affect their function. If the cancer grows in areas like the chest or abdomen, it can press on nearby organs, causing serious problems. Less severe complications may include weakened immunity, making the body more vulnerable to infections. DLBCL may cause blockages in the lymphatic system, leading to fluid buildup or swelling in certain parts of the body. These complications can vary depending on where the cancer spreads.
Symptoms of DLBCL Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
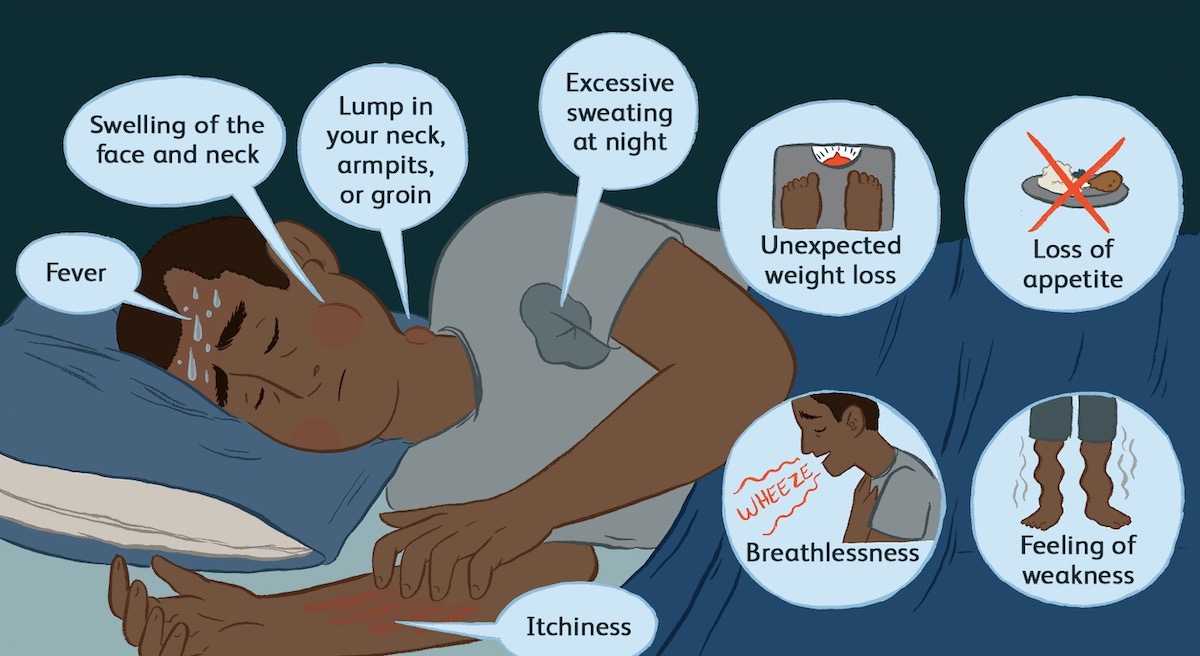
The two most common symptoms of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) are painless swelling of lymph nodes, often in the neck, armpits, or groin, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms occur as the lymphatic system becomes affected by the cancer. Other common symptoms include:
- Fever without infection
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing (if the cancer is in the chest)
- Abdominal pain or swelling (if the cancer is in the abdomen)
How Is It Diagnosed?
This type of cancer is diagnosed through several steps. The steps help doctors confirm the presence of DLBCL and determine how far it has spread.
- Physical exam: A doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes and other signs of the disease.
- Biopsy: This is the most important step. A small sample of tissue, usually from a swollen lymph node, is removed and examined under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
- Blood tests: These tests help assess how well the organs are functioning and look for any abnormalities that may indicate cancer.
- Imaging tests: Scans like CT, PET, or MRI are used to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Sometimes, a sample of bone marrow is taken to check if the cancer has spread to the bone marrow.
Treatment Options for Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
The two most common treatment options are chemotherapy, which uses strong drugs to kill cancer cells, and immunotherapy, which helps the immune system fight the cancer. These treatments are often used together to improve their effectiveness. Other common treatment options include:
- Radiation therapy; using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells
- Targeted therapy; drugs that target specific parts of cancer cells to stop their growth
- Stem cell transplant; replacing damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells after high-dose chemotherapy
If you or a loved one are diagnosed with cancer and are unsatisfied with the treatment plan, it’s wise to seek a second opinion from another hospital or oncology center. Keep exploring to learn more about cancer, the stages of Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and its treatment options. Continue your search here: