Kidney disease is a common health condition that affects millions of people in the United States. It’s a severe medical issue that can have life-threatening complications. However, many people with (chronic) kidney disease – also often referred to as CKD – don’t even know they have it until it’s in the later stages. Because of this, it’s vital to be aware of the risk factors and to talk to your healthcare provider if you’re concerned about your kidney health. By understanding more about kidney problems, you can take steps to protect your kidneys and improve your overall health. Therefore, it’s important to educate yourself on the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, so you can take action to prevent or manage this condition.
What Is Kidney Disease?
Most of us are born with two healthy (i.e., functioning) kidneys on either side of the spine, just slightly above the waist. Your kidneys are crucial organs that help remove waste and extra fluid from your body. It is a health condition when your kidneys don’t work as they should. When they aren’t working properly, waste and fluid can build up in your body and cause problems.
There are two main types: acute kidney disease and chronic kidney disease. Acute kidney disease occurs suddenly and can lead to a sudden loss of kidney function. CKD – also called chronic kidney failure – on the other hand, develops over time and can cause gradual damage to your kidneys. Doctors will call it chronic kidney disease if your kidneys don’t work well for three months or longer.
Causes of (Chronic) Kidney Disease
As previously mentioned, acute kidney disease is caused by a sudden and often temporary problem that affects the kidneys. This can be caused by several factors, including a severe infection or injury, a decrease in blood flow to the kidneys, fluid build-up, or exposure to certain medications or toxins. For example, cases in which these causes can occur include having an enlarged prostate or kidney stones or experiencing a traumatic injury with profound blood loss. CKD is caused by several factors that can damage the kidneys over time. The two most common causes are hypertension (high blood pressure) and diabetes. Other causes include:
- Recurrent kidney infection
- Lupus
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Vesicourethral reflux
- Membranous, or diabetes-related nephropathy
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Glomerulonephritis
Medical researchers have found that certain factors increase the chances of developing CKD. These include having a history of heart disease, a family history of kidney disease, abnormal kidney structure, and being of African-American, Hispanic, Native American, or Asian heritage. Older age is also a risk factor, with people aged 60 or older being more likely to develop CKD. Using painkillers like aspirin and ibuprofen for a long time can also increase the risk of developing this condition. It’s important to be aware of these risk factors and to talk to your healthcare provider if you’re concerned about your kidney health.
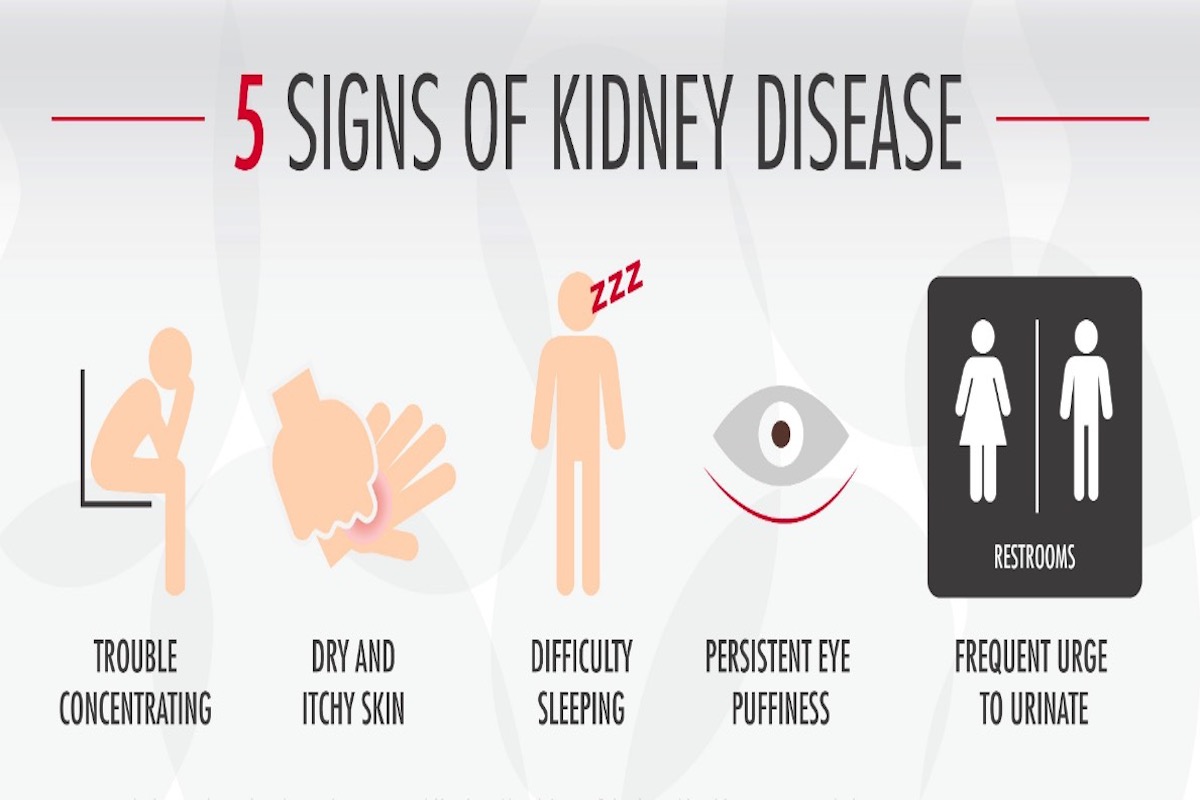
How to Recognize This Medical Condition
Symptoms of (Chronic) Kidney Disease
Symptoms of CKD can vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. The two most common symptoms are fatigue and swelling. Many people with kidney problems feel exhausted and have a lack of energy. This fatigue can be persistent and can interfere with daily activities. Kidney disease can cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in the feet, ankles, hands, and face. Other symptoms of CKD include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty sleeping
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itching and dry skin
- Muscle cramps
- Changes in urine output (more or less than usual)
- Blood in urine
- High blood pressure
- Shortness of breath
Symptoms of Acute Kidney Disease
The symptoms of acute kidney disease can be similar to those of CKD, but they may appear more suddenly and can be more severe. The two most common symptoms are decreased urine output and fluid retention & swelling. Often, one of the first signs is a sudden decrease in the amount of urine produced. Similar to chronic kidney disease, acute kidney disease can also cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in the feet, ankles, hands, and face. Other common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- High blood pressure
- Abdominal pain
- Muscle weakness or cramps
- Changes in heart rate
These kidney conditions can cause a range of complications that affect different parts of the body. Some of the possible complications include high blood pressure, anemia, bone disease, nerve damage, fluid buildup, and kidney failure. High blood pressure can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems. Anemia can occur when the kidneys don’t produce enough red blood cells, which can cause fatigue and weakness. Kidney disease can also lead to bone disease and an increased risk of fractures. Nerve damage can cause tingling, numbness, or weakness in the hands and feet. Fluid buildup can cause shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can lead to kidney failure, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant to treat.
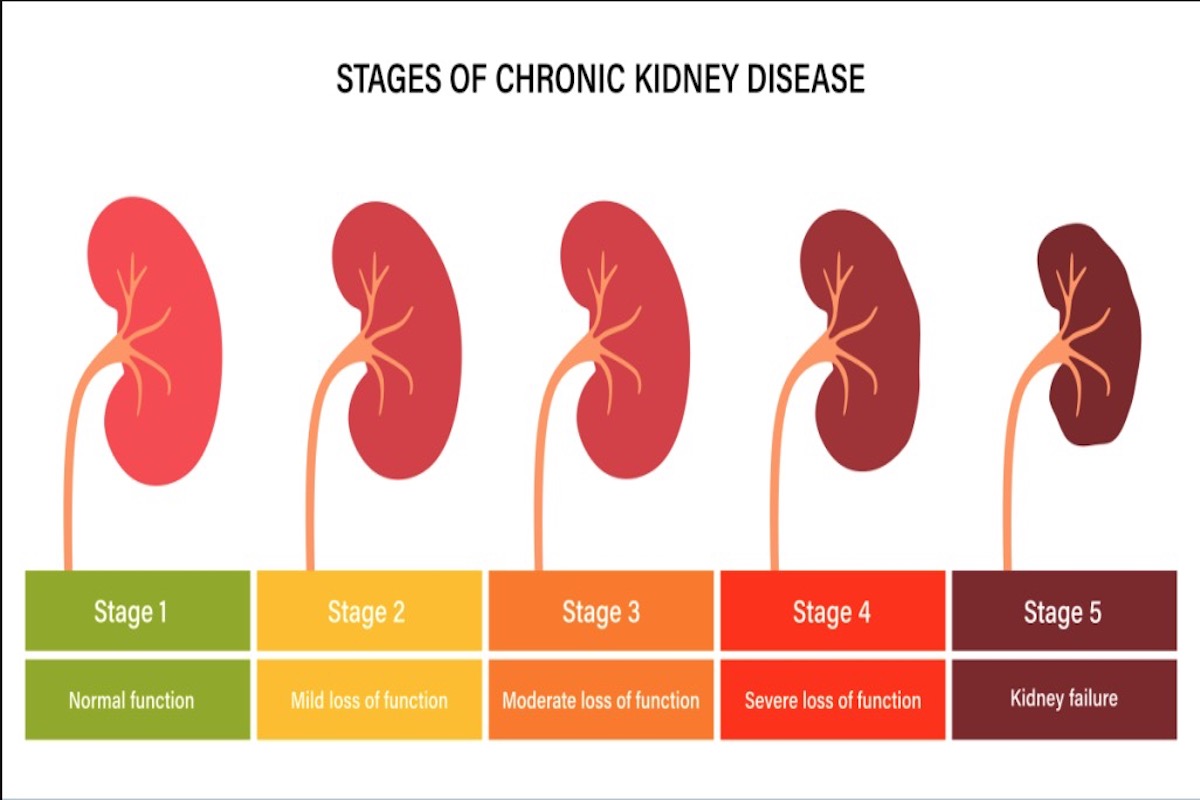
Stages of (Chronic) Kidney Disease
The stages of kidney disease are important to understand how kidneys work and how they can change over time. This condition can be mild or severe, and it’s essential to know the different stages to get the right treatment. To make it easier to understand we’ve created an overview about the stages and GFR,
| Stage of CKD | GFR (ml/min/1.73m²) | What it means |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | ≥ 90 | Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR |
| Stage 2 | 60-89 | Mildly decreased GFR |
| Stage 3a | 45-59 | Mild to moderate decrease in GFR |
| Stage 3b | 30-44 | Moderate to severe decrease in GFR |
| Stage 4 | 15-29 | Severe decrease in GFR |
| Stage 5 | < 15 | Kidney failure (end-stage renal disease) |
GFR stands for glomerular filtration rate, which is a measure of how well the kidneys are functioning. The GFR is calculated based on a person’s age, sex, race, and blood creatinine level. As the GFR decreases, the kidneys are less able to filter waste and fluid from the body. In the early stages of CKD, there may be few or no symptoms, but as the disease progresses, symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and swelling may develop. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider if you’re concerned about your kidney health or if you’re experiencing any symptoms that may be related to kidney disease.
Are There Any Treatment Options?
Kidney disease is diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider. This evaluation involves reviewing your medical history, conducting a physical examination, and performing urine and blood tests. Additionally, imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scan may be used to get a picture of your kidneys and check for any abnormalities. In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be performed to further evaluate the condition of the kidneys. By gathering information from these evaluations, the doctor can determine if you have kidney disease and what stage it is in. Fortunately, there are several treatment options. Of course this depends on the type and stage of the disease. The most common options include:
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to manage underlying health conditions that are contributing to kidney disease, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help manage kidney disease.
- Dialysis: In cases of severe kidney failure, dialysis may be required. Dialysis is a procedure that helps filter waste and extra fluid from the blood when the kidneys are unable to do so.
- Kidney transplant: For severe cases (end-stage), a kidney transplant may be considered as a treatment option. This involves surgically replacing a damaged kidney with a healthy one from a donor.
It’s important to do a lot of research on this condition. You can do this by talking to your professional healthcare provider, as well as through online research. We want to help you along, so start your search here:

