Brain aneurysms are a frequent occurrence in the United States, affecting a substantial number of individuals. On average, around 30,000 people lose their lives each year due to this condition. Understanding a brain aneurysm is crucial for prevention and safeguarding our well-being.
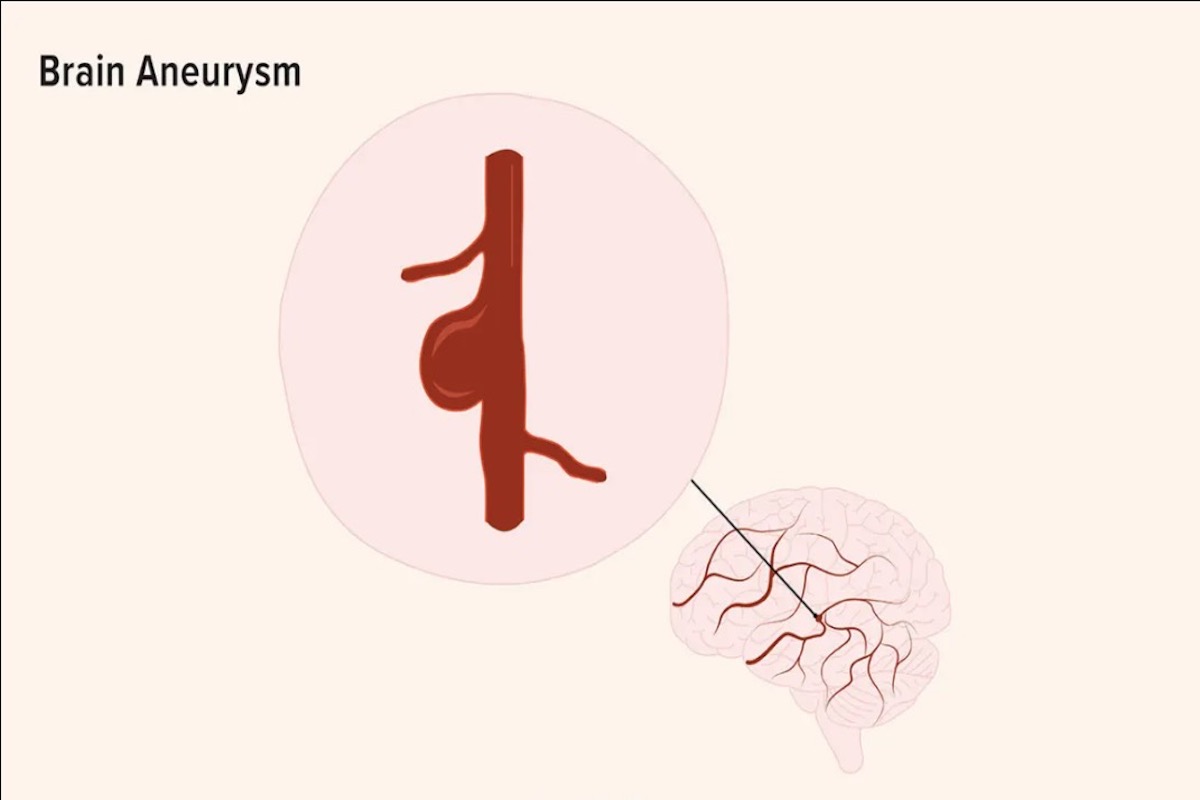
What Is a Brain Aneurysm?
Before we explain symptoms, causes, and possible treatment options, it’s good to know what a brain aneurysm is. In simple terms, a brain aneurysm is like a bulge or balloon that forms in a blood vessel inside the brain. This bulge can become weak and may start to leak or rupture, causing bleeding in the brain. It’s a serious condition because it can lead to stroke or other complications. Detecting and treating brain aneurysms early is important to prevent further damage and ensure better chances of recovery.
Causes of Brain Aneurysm
The exact causes of brain aneurysms are not fully understood, but certain factors can increase the risk. These may include:
- Weak blood vessel walls: Some individuals may have blood vessels that are naturally weaker or more prone to developing aneurysms.
- Family history: A family history of brain aneurysms can increase the likelihood of developing one.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can strain the blood vessel walls and make them more susceptible to aneurysm formation.
- Smoking: Tobacco use, particularly smoking, can weaken blood vessels and contribute to the development of aneurysms.
- Age and gender: Brain aneurysms are more common in individuals over 40 years old, and women are slightly more likely to develop them than men.
- Certain health conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic kidney disease and certain connective tissue disorders, may be associated with an increased risk of aneurysms.
It’s important to note that while these factors can increase the risk, not everyone with these factors will develop a brain aneurysm, and aneurysms can also occur in individuals without any known risk factors.
Undiagnosed complications of brain aneurysms can be very serious. If an aneurysm remains undetected and untreated, it can lead to a rupture or bursting. When this happens, it causes bleeding into the brain, leading to a condition called a subarachnoid hemorrhage. This sudden bleeding can result in severe headaches, loss of consciousness, and even coma. Additionally, it can cause permanent damage to the brain and lead to long-term disabilities such as problems with movement, speech, memory, and coordination. In some cases, the rupture can be life-threatening, causing death or significant neurological impairment. Early diagnosis can help minimize the risks associated with undiagnosed aneurysms.
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysm
brain aneurysm symptoms can vary, but two of the most common ones are sudden and severe headache and vision problems, This may include blurred or double vision, difficulty focusing, or sudden changes in eyesight. There are some other symptoms that people may experience:
- Neck pain or stiffness
- Sensitivity to light
- Loss of consciousness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Difficulty speaking
- Confusion or cognitive changes
Are There Any Treatment Options?
The big question is of course, how are brain aneurysms diagnosed and are there any treatment options? Well, it’sdiagnosed through different methods. The professional healthcare provider will ask about the person’s symptoms and do a physical examination. Imaging tests such as MRI and CT scans are used to create pictures of the brain and find the aneurysm. Sometimes, a special test called cerebral angiography is done, which involves injecting dye into the blood vessels to see them more clearly. These tests help the doctors identify the presence, size, and location of the aneurysm, which is important for deciding the best treatment options. These treatments include:
- Observation: If the aneurysm is small and not causing symptoms, the doctor may choose to closely monitor it over time with regular imaging tests to check for any changes.
- Endovascular coiling: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a catheter through a blood vessel in the groin and guiding it to the aneurysm. Tiny platinum coils are then placed in the aneurysm to promote blood clotting and prevent rupture.
- Surgical clipping: In this procedure, a section of the skull is temporarily removed to access the aneurysm directly. A metal clip is then placed around the neck of the aneurysm to stop the blood flow and prevent rupture.
- Flow diversion: This newer technique involves placing a stent-like device called a flow diverter across the neck of the aneurysm. It redirects blood flow and promotes healing of the aneurysm.
We know, it can be a challenging problem to deal with, but there are solutions available. Identifying the cause and seeking the right treatment for your situation is important. We hope this article has provided helpful information on how to deal with a brain aneurysm. For more info on this topic, or other tips start your search here:

