Atopic dermatitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people in the United States. It is also known as eczema, characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. This skin condition is most common in children, but it can affect people of all ages. In fact, it is estimated that around 31.6 million people in the United States have some form of eczema. While there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, there are various treatments and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Before we tell you this, it’s important to know how you can recognize the skin condition and what causes it.
What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
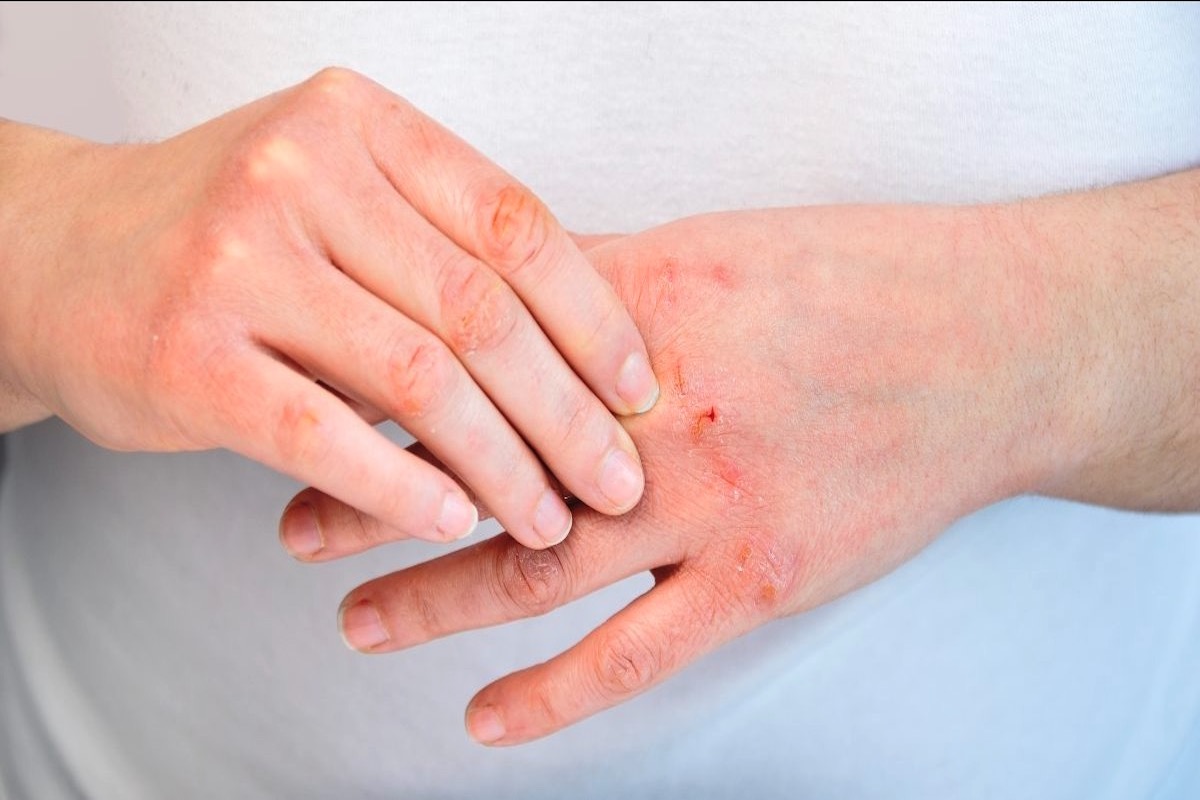
Atopic dermatitis is a skin condition that can cause dry, scaly, and itchy skin. It’s a chronic condition, which means it can last for a long time and may come and go over a person’s lifetime. This condition can affect people of all ages, but it’s more common in children. The appearance can vary depending on a person’s skin color. For people with light-colored skin, it often appears as red rashes, while those with darker skin may develop brown, purple, or gray rashes. Despite the physical discomfort and appearance, it can also significantly impact a person’s emotional well-being.
Causes & Triggers of Atopic Dermatitis
What causes this skin condition is not fully understood, but it is believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. For example, if a person has a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies, they may be more likely to develop atopic dermatitis. Additionally, certain environmental factors, such as exposure to harsh chemicals or changes in temperature and humidity, can trigger or worsen the condition.
Triggers are things that can cause or worsen atopic dermatitis. Several triggers can affect different people in different ways. Some common triggers include:
- Skin irritants such as soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics.
- Dry skin can cause itching and lead to a flare-up.
- Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander.
- Stress, which can weaken the immune system and trigger a flare-up.
- Changes in temperature or humidity, which can cause the skin to become dry and itchy.
- Certain foods or food additives, such as eggs, dairy products, and preservatives.
- Exposure to certain chemicals or substances, such as tobacco smoke, perfumes, or solvents.
By identifying and avoiding triggers, someone with atopic dermatitis can help manage their symptoms and prevent flare-ups. It is important to note that triggers can vary from person to person, and not all triggers will affect everyone in the same way. Continue reading on the next page for more informatin about this skin condition.

